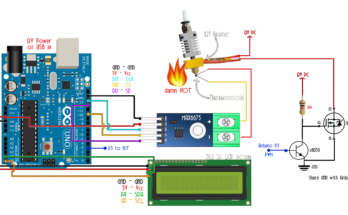
RFID Train Passenger Authentication System Arduino and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) form the foundation of today’s industrial automation. These durable and intelligent devices are engineered to manage electrical machines with high efficiency, offering enhanced reliability, adaptability, and accuracy across a wide range of applications.
1. What is a PLC?

A Motorized Curtain System using DC Motor, Push Buttons, and Arduino Uno shares similar automation principles with a PLC, which is a specialized industrial digital computer designed to control processes automatically. Unlike standard computers, PLCs are built to withstand harsh industrial conditions and provide real-time control of machinery. They interpret signals from sensors, perform logic-based decisions, and activate outputs to operate various types of equipment.
2. Why Use PLCs in Electrical Machine Control?

PLCs provide several advantages that make them essential in industrial settings:
- Reliability: They are built to withstand harsh conditions such as high temperatures, vibrations, and electrical noise.
- Flexibility: PLCs can be reprogrammed easily to adapt to different control requirements.
- Scalability: They can manage anything from a single machine to an entire factory floor.
- Precision: With real-time processing, PLCs ensure highly accurate control over machine functions.
3. Key Functions of PLCs in Machine Control

They are used in various applications, including:
- Motor Control: Regulating speed, torque, and direction of electric motors.
- Process Automation: Managing complex industrial processes like conveyor systems and assembly lines.
- Monitoring & Data Logging: Collecting real-time data for performance analysis and maintenance.
- Fault Detection: Identifying errors and triggering alarms to prevent damage.
4. Components of a PLC System

A typical PLC system consists of:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): Executes logic instructions and processes data.
- Input/Output (I/O) Modules: Interfaces with sensors, switches, and actuators.
- Memory: Stores programs and operational data.
- Communication Ports: Enables connectivity with other systems for remote control and monitoring.
5. Future of PLCs in Industrial Automation

With advancements in Industrial IoT (IIoT) and AI, PLC are becoming smarter. Modern PLC integrate with cloud-based systems, allowing remote monitoring and predictive maintenance, enhancing overall machine efficiency.
Conclusion
PLCs are indispensable in electrical machine control, providing automation, efficiency, and reliability. As industries continue to evolve, PLCs will play a crucial role in shaping the future of smart manufacturing.