Introduction
Techniques for Improving Memory and Learning as an art and science that has been used for centuries to improve memory and learning efficiency. Mnemonics are tools and techniques that transform mundane information into memorable content. In this article, we explore the art of mnemonics, uncovering various strategies and their profound impact on memory and education.
What Are Mnemonics?
Definition of Mnemonics

Mnemonics are memory aids designed to make information easier to remember. They work by associating unfamiliar data with familiar cues such as images, phrases, or patterns.
Historical Significance of Mnemonics
Dating back to ancient Greece, mnemonics have been integral in oral traditions and memory training, used by scholars and storytellers to pass down vast amounts of knowledge.
Why Mnemonics Work
The Brain’s Preference for Patterns
Our brains are wired to recognize patterns, stories, and associations. Mnemonics exploit this tendency by linking information to vivid imagery, sequences, or rhythmic patterns.
Enhancing Neural Connections
By associating new information with existing knowledge, mnemonics strengthen neural pathways, making recall faster and more reliable.
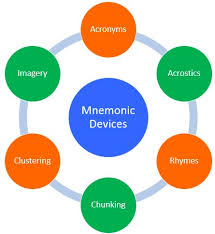
Types of Mnemonics
Visual Mnemonics
Using imagery to represent information—for example, imagining a rainbow for the colors of the spectrum (ROYGBIV).
Acronyms and Initialisms
Creating a word or phrase where each letter represents a piece of information, like “HOMES” for the Great Lakes (Huron, Ontario, Michigan, Erie, Superior).
Rhymes and Songs
Rhythmic patterns, such as “30 days hath September…” make sequences easier to remember.
Chunking
Breaking information into smaller, manageable groups, like remembering phone numbers in sets of three or four digits.
Method of Loci
Associating information with specific physical locations in a familiar place, such as rooms in your house.
Techniques for Improving Memory with Mnemonics
Storytelling
Turning information into a narrative makes it more engaging and memorable. For instance, creating a story to remember the order of planets in the solar system.
Linking Technique
Connecting items to each other in a logical or absurd sequence. For example, linking grocery items by visualizing them interacting (milk pouring into bread).
Peg System
Using a predetermined list of pegs (e.g., numbers associated with rhyming words) to recall information by associating each item with a peg.
Visualization and Association
Creating mental images to link facts or concepts, making them stand out vividly in your mind.
Benefits of Mnemonics
Improved Memory Retention
Mnemonics help retain information longer by embedding it into meaningful patterns.
Enhanced Learning Efficiency
By simplifying complex data, mnemonics make learning faster and more engaging.
Boosted Confidence
Remembering details accurately fosters self-assurance, whether in academics, work, or daily life.
Accessibility for All Ages
Mnemonics are universal, benefiting children, students, professionals, and the elderly alike.
Mnemonics in Education
Helping Students Retain Facts
Mnemonics simplify memorization of historical dates, scientific terms, or mathematical formulas.
Language Learning
Remembering vocabulary, grammar rules, or conjugations becomes easier with mnemonic devices.
Test Preparation
Mnemonic strategies assist students in recalling large volumes of information during exams.
Examples of Mnemonics in Everyday Use
Medical Mnemonics
Medical students use mnemonics to recall anatomy, like “On Old Olympus Towering Tops…” for cranial nerves.
Navigation
“Never Eat Soggy Waffles” helps recall compass directions (North, East, South, West).
Music and Arts
Musicians learn scales using mnemonics like “Every Good Boy Does Fine” for the treble clef lines.
Challenges of Using Mnemonics
Over-reliance on Mnemonics
Focusing solely on memory aids can hinder deeper understanding of the material.
Creation Time
Designing effective mnemonics can be time-intensive.
Personalization
Not all mnemonic methods resonate with everyone; trial and error may be required.
Advancing Mnemonics with Technology
Memory Apps
Apps like Anki and Quizlet use mnemonic strategies to optimize learning and recall.
Gamification
Memory games employ mnemonics to make learning interactive and fun.
Virtual Reality (VR)
Using VR environments for techniques like the Method of Loci enhances spatial memory training.
The Role of Mnemonics in Cognitive Health
Fighting Memory Loss
Mnemonics can be therapeutic for individuals with memory impairments, such as those with dementia or Alzheimer’s disease.
Encouraging Lifelong Learning
Using mnemonics promotes continuous mental engagement and cognitive flexibility.
Myths About Mnemonics
“Mnemonics Are Only for Memorizing Facts”
In reality, mnemonics can also help develop understanding and creative thinking by linking concepts innovatively.
“Mnemonics Are a Shortcut”
While they simplify memory tasks, mnemonics still require practice and active engagement to be effective.
Personal Reflections on Mnemonics
Exploring mnemonics has been transformative in understanding the intricacies of memory. From simple acronyms to the sophisticated Method of Loci, these tools showcase the power of creativity in learning. They emphasize that memory isn’t just about rote recall—it’s about finding meaning and connections that make knowledge come alive.
Conclusion
The art of mnemonics is more than just a memory trick—it’s a gateway to better learning and understanding. Whether you’re a student preparing for exams, a professional juggling information, or someone looking to enhance cognitive health, mnemonics offer practical and engaging solutions. With the right techniques and practice, anyone can unlock their memory’s full potential.
Also: Netflix & Chill: 10 Must Watch Rom-Coms of the Early 2000s
Meta Description
“Discover the art of mnemonics! Explore techniques like acronyms, visualization, and the Method of Loci to improve memory and enhance learning efficiency.”
FAQs
1. What is the purpose of mnemonics?
Mnemonics are designed to simplify information recall by associating it with patterns, images, or familiar cues.
2. Can mnemonics help with long-term memory?
Yes, when practiced consistently, mnemonics can improve long-term retention by embedding information in meaningful associations.
3. Are mnemonics effective for all age groups?
Absolutely! Mnemonics benefit children, adults, and seniors alike, making them versatile memory tools.
4. What is the most popular mnemonic technique?
Techniques like acronyms and the Method of Loci are widely used for their simplicity and effectiveness.
5. How can I create my own mnemonics?
Start by identifying key information and associating it with vivid images, patterns, or stories that are personally meaningful to you.