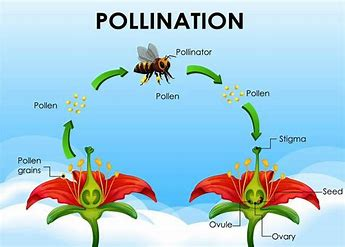
Pollination, the transfer of pollen from the male part of a flower to the female part, is a critical process for fruit and seed production in many crops. Efficient pollination directly translates to higher yields and better quality produce.

Read More: IoT-Based Early Warning Systems for Frost Detection in Orchards
However, factors like habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change are impacting pollinator populations, making it crucial for farmers to adopt smart strategies to enhance pollination efficiency. This post explores some key smart farming practices that can significantly improve pollination in agricultural settings.
The Importance of Pollination in Agriculture
Pollination is essential for the reproduction of many crops, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. Without adequate pollination, these plants cannot produce viable fruit or seeds, leading to significant crop losses.
Read More: Precision Agriculture Techniques for Enhancing Organic Farming
While some plants are self-pollinating, many rely on external agents like insects (bees, butterflies, moths), birds, bats, and wind for cross-pollination. Ensuring efficient pollination is therefore vital for food security and agricultural sustainability.
Smart Farming Practices for Enhanced Pollination
Read More: AI-Powered Soil Analysis for Precision Nutrient Management: Revolutionizing Agriculture
Smart farming leverages technology and data-driven approaches to optimize agricultural practices, including pollination. Here are some key strategies:
1. Creating Pollinator Habitats:
- Flower Strips and Hedgerows: Planting diverse flowering plants along field edges or within the farm creates attractive habitats for pollinators, providing them with food (nectar and pollen) and shelter. Choose native plant species that bloom at different times throughout the growing season to provide a continuous food source.
- Reduced Tillage: Minimizing soil disturbance helps protect ground-nesting bees and other beneficial insects.
- Nesting Sites: Providing artificial nesting sites, such as bee hotels or undisturbed patches of bare ground, can further encourage pollinator populations.
2. Optimizing Pesticide Use:
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Implementing IPM strategies focuses on preventing pest problems through a combination of methods, including biological control, cultural practices, and targeted pesticide applications only when necessary.
- Timing of Applications: Avoid applying pesticides during peak pollinator activity, such as during flowering periods. If pesticide application is unavoidable, apply it in the evening or early morning when pollinators are less active.
- Selective Pesticides: Choose pesticides that are less toxic to pollinators and avoid broad-spectrum insecticides that can harm beneficial insects.
3. Utilizing Technology for Pollination Monitoring and Management:
- Sensor Networks: Deploying sensors to monitor environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and wind speed can help predict pollinator activity and optimize pollination conditions.
- Drone Technology: Drones can be used for targeted pollen dispersal or to monitor pollinator activity and identify areas with insufficient pollination.
- Precision Agriculture: Using GPS and other technologies to map and manage fields can help optimize crop placement and create better connectivity between pollinator habitats and crop areas.
4. Supporting Managed Bee Colonies:
- Hive Placement: Strategically placing beehives within or near crop fields can significantly enhance pollination, especially for crops that rely heavily on bee pollination.
- Collaboration with Beekeepers: Working with local beekeepers can ensure a reliable supply of healthy bee colonies for pollination services.
5. Diversifying Crops and Farming Systems:
- Crop Rotation: Rotating different crops can create a more diverse and stable environment for pollinators.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees into farming systems can provide additional habitat and food sources for pollinators.
Benefits of Enhancing Pollination Efficiency
- Increased Crop Yields: Improved pollination directly leads to higher fruit and seed set, resulting in increased yields.
- Improved Fruit Quality: Adequate pollination can improve fruit size, shape, and overall quality.
- Enhanced Biodiversity: Supporting pollinator populations contributes to overall biodiversity and ecosystem health.
- Increased Farm Profitability: Higher yields and better quality produce translate to increased farm income.
Conclusion
By adopting smart farming practices that prioritize pollinator health and enhance pollination efficiency, farmers can significantly boost their yields, improve the quality of their produce, and contribute to a more sustainable agricultural system. Implementing these strategies is not only beneficial for individual farms but also crucial for ensuring global food security in the face of ongoing environmental challenges.


