In the ever-evolving landscape of medical technology, innovations continue to reshape the way we approach diagnosis and treatment. How Positron Emission Tomography Microchip Works represent a cutting-edge development, promising to revolutionize the field of medical imaging.
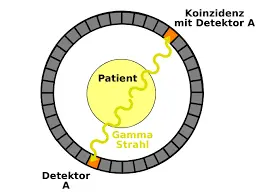
Positron emission tomography (PET) microchip has revolutionized medical imaging, providing invaluable insights into the body’s metabolic activity. This sophisticated technique utilizes radioisotopes to generate detailed images of functional processes, aiding in the diagnosis, staging, and treatment monitoring of a wide range of diseases. At the heart of PET technology lies a crucial component: the PET microchip.
Understanding Positron Emission Tomography Microchips: A Technological Breakthrough
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) microchips, also known as PET tracer micro implants, are small, implantable devices that play a vital role in enhancing the accuracy and sensitivity of PET scans. These microchips contain radioactive tracers, such as fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), which are selectively taken up by metabolically active tissues, particularly cancer cells.
The Mechanism of Positron Emission Tomography Microchips: Tracking Metabolic Activity
When injected into the bloodstream, the radioactive tracer circulates throughout the body and accumulates in areas of high metabolic activity. The PET microchips, strategically implanted in specific tissues or tumors, act as localized detectors, capturing the emitted gamma rays from the decaying radiotracer.
Applications of Positron Emission Tomography Microchips: Expanding Diagnostic Horizons

PET microchips offer a diverse range of applications in medical imaging, complementing traditional PET scans and expanding their diagnostic capabilities:
- Tumor Detection and Localization: PET microchips can provide precise information about the location, size, and metabolic activity of tumors, aiding in early cancer detection and staging.
- Monitoring Cancer Treatment Response: PET microchips can assess the effectiveness of cancer treatment by tracking changes in tumor metabolism, allowing for timely adjustments in treatment strategies.
- Drug Development and Evaluation: PET microchips can monitor the distribution and metabolism of drugs in the body, providing valuable insights into drug efficacy and pharmacokinetics.
- Neurological Disorders Research: PET microchips can visualize brain activity and metabolic changes associated with neurological disorders, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Benefits of PET Microchips: Enhancing PET Imaging

PET microchips offer several advantages over traditional PET scans:
- Improved Accuracy: PET microchips provide localized measurements of metabolic activity, reducing background noise and enhancing the accuracy of PET scans.
- Real-Time Monitoring: PET microchips enable real-time monitoring of metabolic activity, allowing for dynamic assessment of physiological processes.
- Reduced Radiation Exposure: PET microchips require lower doses of radioactive tracers, minimizing radiation exposure to patients.
The Future of PET Microchips: A Promising Outlook
Research and development efforts are continuously advancing PET microchip technology, addressing current limitations and expanding their applications:
- Miniaturization: Researchers are working on developing smaller, more biocompatible PET microchips for wider applications.
- Multimodality Imaging: Efforts are underway to integrate PET microchips with other imaging modalities, providing comprehensive anatomical and functional information.
- Personalized Medicine: PET microchips hold promise in guiding personalized treatment plans based on individual tumor metabolism.
Challenges of PET Microchips: Addressing Limitations
Despite their significant contributions, PET microchips face certain challenges:
- Limited Coverage: PET microchips can only provide information about specific tissues or tumors where they are implanted.
- Cost Considerations: The development and implementation of PET microchips involve substantial costs.
- Regulatory Requirements: PET microchips require strict regulatory approval and standardization to ensure their safety and efficacy.
Conclusion: Revolutionizing Medical Imaging with PET Microchips
PET microchips have emerged as transformative tools in medical imaging, enhancing the accuracy and sensitivity of PET scans and expanding their diagnostic capabilities. Their applications span a wide range of diseases, from cancer to neurological disorders, providing valuable insights into the body’s metabolic activity. As research and development continue to refine PET microchip technology, their impact on medical imaging is poised to grow even further, revolutionizing the way we diagnose, monitor, and treat diseases.
Read More:
- The Technology That Determines World Power: Semiconductors
- 3D Objects Made With Sound
- Eating Right | Why And Benefits OF Healthy Eating
- BEST FRUITS TO CONSIDER FOR A HEALTHY DIET
- How PET Scans Work: A Comprehensive Guide


