Introduction

Africa, often referred to as the “Cradle of Humankind,” boasts a rich and diverse history that has significantly influenced the world. The early rise and development of African civilizations are testament to the continent’s vast cultural heritage and ingenuity. Let’s dive into this fascinating journey of Africa’s early civilizations, exploring their unique contributions and lasting legacies. yes, let us talk about earliest civilization in Africa.
The Kingdom of Kush
Origins of Kush
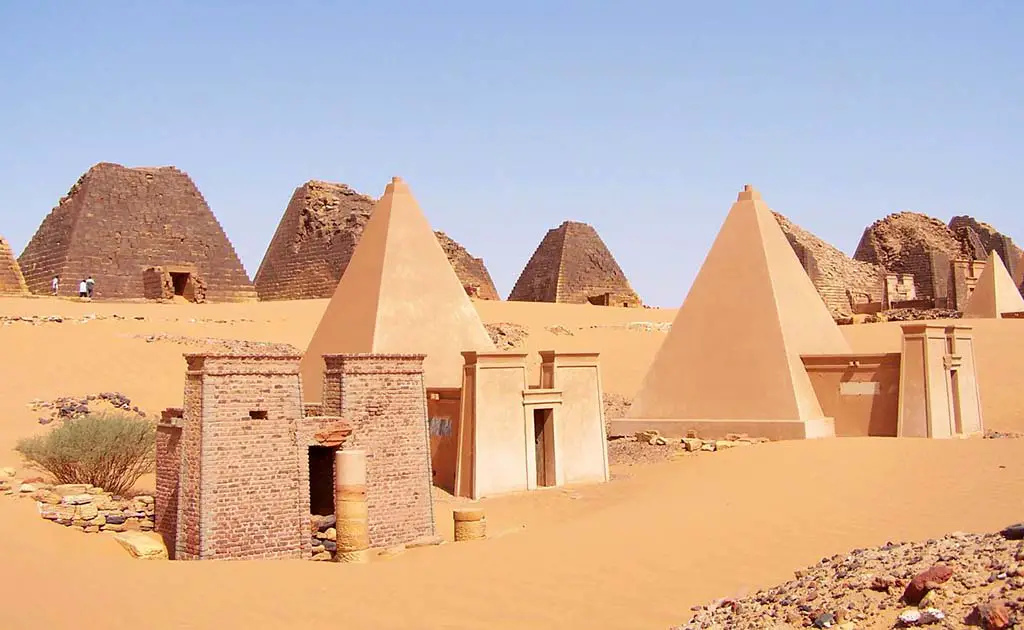

Kush, an ancient Nubian kingdom, thrived along the Nile River. Its roots can be traced back to around 1070 BCE, following the collapse of the Egyptian New Kingdom. Kushites were adept at harnessing the Nile’s resources, which fueled their growth.
Kushite Culture and Achievements

The Kingdom of Kush is renowned for its impressive pyramids, which rival those of Egypt. These structures were not only tombs but also symbols of the Kushite’s architectural prowess. Additionally, Kushites were skilled in ironworking, which gave them a technological edge in warfare and agriculture.
Read Also The History of Free Love: How the Sexual Revolution Shaped Modern Relationships
Kush and Egypt: A Complex Relationship
Kush and Egypt shared a complex relationship marked by both conflict and cooperation. At various times, Kushite pharaohs ruled Egypt, creating a unique blend of cultures that enriched both civilizations.
The Kingdom of Aksum
Rise of Aksum

Aksum, located in present-day Ethiopia and Eritrea, emerged as a powerful trading empire around the 1st century CE. Its strategic position enabled it to control key trade routes connecting Africa, Asia, and Europe.
Aksumite Innovations

Aksumites were pioneers in coinage, being the first African civilization to mint their own currency. This innovation facilitated trade and economic stability. They also developed a unique script, Ge’ez, which remains in use today in the Ethiopian Orthodox Church.
The Decline of Aksum
Despite its early successes, Aksum’s decline began in the 7th century CE due to a combination of environmental changes, trade route shifts, and conflicts with neighboring states.
The Ghana Empire
Foundations of Ghana

The Ghana Empire, located in West Africa, flourished between the 6th and 13th centuries CE. It was known for its wealth, which stemmed from its vast gold mines and control over trans-Saharan trade routes.
The Role of Trade in Ghana
Trade played a crucial role in Ghana’s prosperity. The empire’s strategic location enabled it to facilitate the exchange of gold, salt, and other goods between North Africa and the sub-Saharan region.
H4: Ghana’s Social Structure

Ghana had a complex social structure, with a king who wielded significant power and authority. The king was supported by a network of nobles and officials who helped administer the empire.
The Mali Empire

The Rise of Mali
The Mali Empire, which succeeded Ghana, reached its zenith during the 13th and 14th centuries CE. It was founded by the legendary Sundiata Keita, who united various tribes and established a strong central government.
Mansa Musa: The Wealthiest Man in History

Mansa Musa, one of Mali’s most famous rulers, is often regarded as the wealthiest man in history. His pilgrimage to Mecca in 1324 CE showcased Mali’s immense wealth and put the empire on the global map.
H4: Mali’s Educational and Cultural Contributions
Mali was a hub of learning and culture. The city of Timbuktu, in particular, was renowned for its universities and libraries, attracting scholars from across the Islamic world.
you may also like From Signals to Smartphones: A Communication Journey
The Songhai Empire

Songhai’s Expansion
The Songhai Empire, which rose to prominence in the 15th century CE, was one of the largest empires in African history. Under the leadership of rulers like Sonni Ali and Askia Muhammad, Songhai expanded its territories and consolidated its power.
Songhai’s Economic and Military Strength

Songhai’s economy was driven by trade, agriculture, and mining. The empire’s military strength was also noteworthy, with a well-organized army that utilized both cavalry and infantry units.
You May Also Read; Tech Titans: Innovations Reshaping Modern Combat
The Fall of Songhai
Songhai’s decline began in the late 16th century CE, due to internal strife and external pressures from invading forces such as the Moroccans.
The Great Zimbabwe

Architectural Marvels of Great Zimbabwe

Great Zimbabwe, located in southeastern Africa, is known for its impressive stone structures, which were built between the 11th and 15th centuries CE. These structures, including the Great Enclosure, highlight the architectural and engineering skills of its inhabitants.
The Economy of Great Zimbabwe
The economy of Great Zimbabwe was based on agriculture, cattle herding, and trade. The region’s wealth was further augmented by the control of gold mines and trade routes.
The Mystery of Great Zimbabwe’s Decline
The decline of Great Zimbabwe remains a mystery, but it is believed to have been caused by a combination of environmental factors, overpopulation, and political instability.
The Swahili Coast

The Rise of Swahili City-States
The Swahili Coast, stretching along the eastern shores of Africa, saw the emergence of prosperous city-states such as Kilwa, Mombasa, and Zanzibar. These city-states thrived between the 10th and 16th centuries CE.
Trade and Cultural Exchange on the Swahili Coast

The Swahili Coast was a melting pot of cultures, with influences from Africa, Arabia, Persia, and India. Trade was the lifeblood of these city-states, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies.
The Impact of European Exploration
The arrival of European explorers and traders in the late 15th century CE marked a significant turning point for the Swahili Coast. The subsequent colonization and exploitation disrupted the region’s trade networks and political structures.
Conclusion
The early civilizations of Africa were characterized by their resilience, innovation, and cultural richness. From the architectural marvels of Great Zimbabwe to the scholarly pursuits of Timbuktu, these civilizations laid the foundation for Africa’s rich and diverse heritage. Understanding this history is crucial in appreciating the continent’s contributions to the global tapestry of human civilization.
FAQs
1. What were the major achievements of the Kingdom of Kush?
The Kingdom of Kush is renowned for its impressive pyramids, advancements in ironworking, and its complex relationship with Egypt, which included periods of Kushite rule over Egypt.
2. How did the Mali Empire become so wealthy?
The Mali Empire’s wealth primarily came from its vast gold mines and control over trans-Saharan trade routes. Mansa Musa’s reign further showcased the empire’s immense wealth through his legendary pilgrimage to Mecca.
3. What led to the decline of the Songhai Empire?
The decline of the Songhai Empire was due to internal strife and external pressures from invading forces, particularly the Moroccans, in the late 16th century CE.
4. What made the Swahili Coast a unique cultural melting pot?
The Swahili Coast’s strategic location facilitated trade and cultural exchange between Africa, Arabia, Persia, and India, making it a vibrant and diverse region.
5. Why is Timbuktu significant in African history?
Timbuktu was a hub of learning and culture, renowned for its universities and libraries, which attracted scholars from across the Islamic world. It played a crucial role in the intellectual and cultural life of the Mali Empire.