
Introduction
As the effects of climate change become increasingly evident—ranging from extreme weather events to rising sea levels—there is an urgent need for innovative solutions to mitigate its impact. Technology has emerged as a powerful ally in this battle, offering tools and strategies that can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable practices. This article explores groundbreaking innovations across various sectors, examining how they can help combat climate change and pave the way for a more sustainable future.
Read Blast from the Past: The Technologies That Time Forgot
The Role of Renewable Energy
- Solar Power: Harnessing the Sun
- Solar energy is one of the most promising renewable resources available today. With advancements in photovoltaic technology, solar panels have become more efficient and affordable, making solar power accessible to both residential and commercial users.

- Impact on Emissions: By transitioning from fossil fuels to solar energy, we can drastically reduce carbon emissions. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), solar power could account for nearly 25% of global electricity generation by 2030.
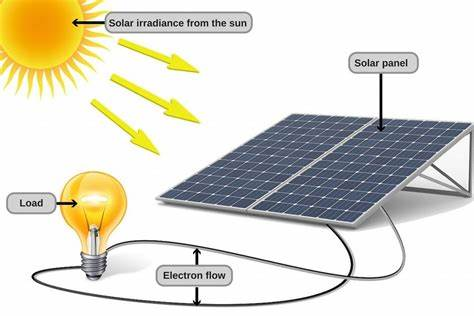
- Wind Energy: Powering the Future
- Wind turbines have evolved significantly over the past few decades, with larger and more efficient designs capable of generating substantial amounts of electricity. Offshore wind farms are particularly promising due to their higher wind speeds and reduced land use conflicts.
- Economic Benefits: The wind energy sector has also proven to be a significant job creator, providing employment opportunities while contributing to local economies.

- Hydrogen Fuel: The Clean Energy Carrier
- Hydrogen has gained attention as a clean energy carrier that can be produced from renewable sources through electrolysis. When burned or used in fuel cells, hydrogen emits only water vapor, making it an attractive alternative to fossil fuels.
- Potential Applications: Hydrogen can power vehicles, heat buildings, and even serve as a feedstock for industrial processes, offering a versatile solution for various sectors.

Smart Technologies for Energy Efficiency
- Smart Grids: Revolutionizing Energy Distribution
- Smart grid technology enhances the efficiency of electricity distribution by utilizing digital communication tools to monitor and manage energy flow. This allows for better integration of renewable energy sources and real-time adjustments based on demand.
- Benefits: By reducing energy waste and improving reliability, smart grids can significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation.
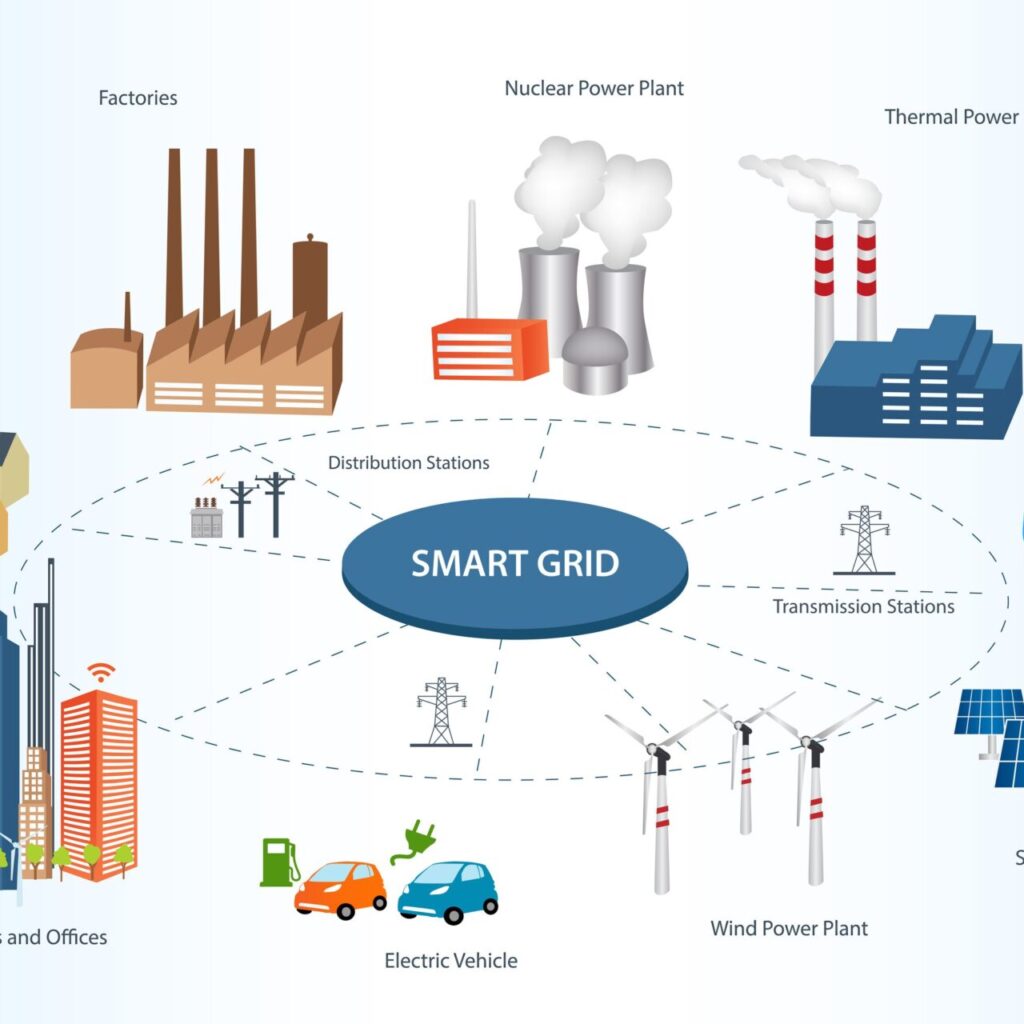
- Energy-Efficient Buildings: Sustainable Design
- Innovations in building materials and design have led to the development of energy-efficient buildings that consume less power for heating, cooling, and lighting. Techniques such as passive solar design and green roofs contribute to lower energy consumption.
- Long-Term Savings: While initial construction costs may be higher, energy-efficient buildings often result in significant savings on utility bills over time.
- Smart Home Technologies: Empowering Consumers
- Smart home devices such as thermostats, lighting systems, and appliances enable consumers to monitor and control their energy usage more effectively. These technologies promote energy conservation by optimizing consumption patterns.
- User Engagement: By providing real-time feedback on energy usage, smart home technologies encourage users to adopt more sustainable habits.
Innovations in Transportation
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Reducing Emissions on the Road
- The rise of electric vehicles represents a significant shift in transportation technology. With advancements in battery technology leading to longer ranges and faster charging times, EVs are becoming increasingly viable for consumers.
- Environmental Impact: Transitioning from internal combustion engines to EVs can drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions from one of the largest contributing sectors—transportation.
- Public Transportation Solutions: Sustainable Mobility
- Innovations in public transportation systems—such as electric buses and light rail—offer sustainable alternatives to traditional fossil-fuel-powered transit options. These systems reduce congestion and lower emissions while providing efficient mobility solutions.
- Community Benefits: Improved public transportation can enhance accessibility for communities while promoting economic growth through increased mobility.
- Shared Mobility Services: Reducing Vehicle Ownership
- Ride-sharing platforms and car-sharing services have gained popularity as alternatives to personal vehicle ownership. By promoting shared mobility, these services can decrease traffic congestion and reduce overall emissions.
- Urban Planning: Integrating shared mobility solutions into urban planning can lead to more sustainable cities with reduced reliance on personal vehicles.
Agriculture and Land Management Innovations
- Climate-Smart Agriculture: Sustainable Practices
- Climate-smart agriculture focuses on increasing productivity while reducing greenhouse gas emissions through sustainable practices such as crop rotation, agroforestry, and precision farming.
- Food Security: By improving resilience against climate change impacts, these practices ensure food security for growing populations while minimizing environmental degradation.
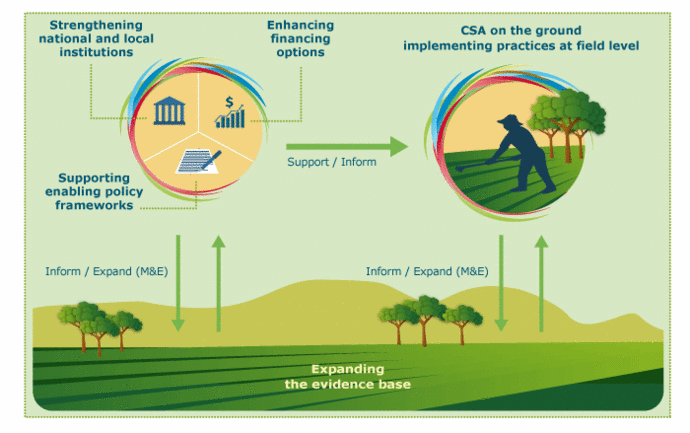
- Vertical Farming: Maximizing Space Efficiency
- Vertical farming utilizes innovative techniques such as hydroponics and aeroponics to grow crops in controlled environments stacked vertically. This method reduces land use while minimizing water consumption.
- Urban Agriculture: Vertical farms can be integrated into urban areas, providing fresh produce locally while reducing transportation emissions associated with food distribution.
- Reforestation Technologies: Restoring Ecosystems
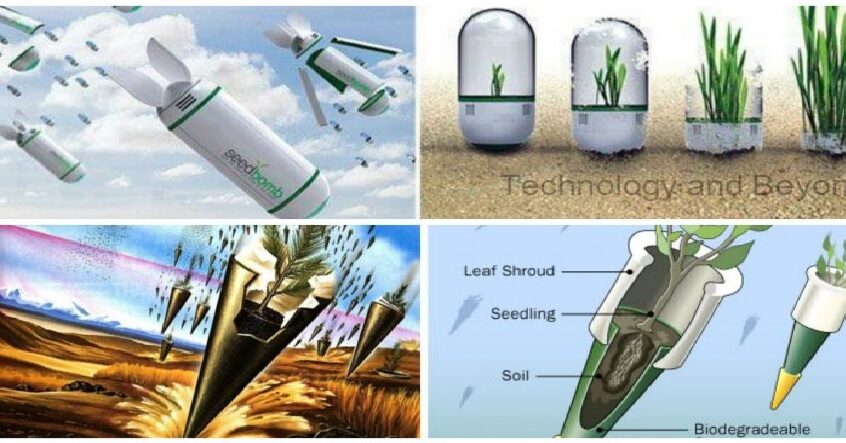
- Innovative reforestation techniques—including drone planting—enable rapid restoration of forests that have been lost due to deforestation or natural disasters. These efforts not only sequester carbon but also restore biodiversity.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in reforestation projects fosters stewardship of natural resources while providing economic opportunities through eco-tourism or sustainable forestry.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
- AI in Climate Modeling: Predicting Changes
- Artificial intelligence is transforming climate modeling by analyzing vast datasets to improve predictions about climate change impacts. AI algorithms can identify patterns that human researchers may overlook, enhancing our understanding of complex systems.
- Disaster Preparedness: Improved climate models enable better preparation for extreme weather events by providing early warning systems that save lives and minimize damage.
- Optimizing Resource Management with AI
- AI technologies are being employed in various sectors—such as agriculture, water management, and energy—to optimize resource usage and reduce waste.
- Efficiency Gains: For example, AI-driven irrigation systems can monitor soil moisture levels in real-time, ensuring that crops receive just the right amount of water needed for optimal growth.
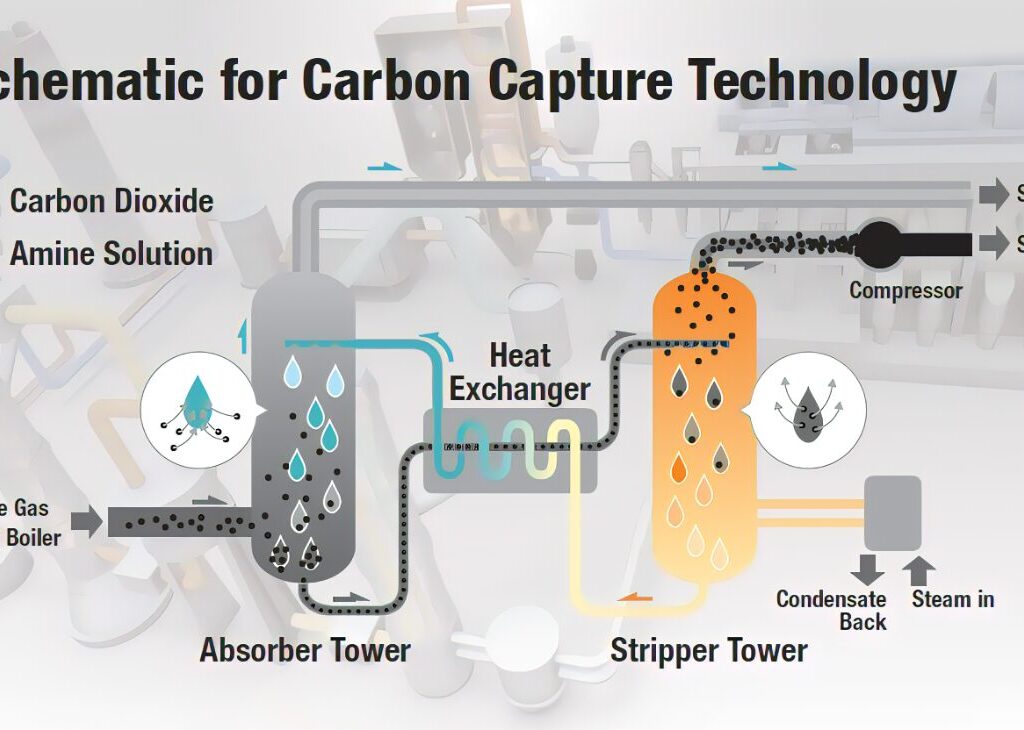
- Carbon Capture Technologies Powered by AI
- Innovations in carbon capture technology are enhanced by AI algorithms that optimize capture processes and improve efficiency in removing CO2 from the atmosphere.
- Scalability Potential: As these technologies mature, they hold promise for significantly reducing atmospheric carbon levels when integrated into industrial processes.
Conclusion
The fight against climate change requires immediate action coupled with innovative technological solutions across multiple sectors. From renewable energy sources like solar and wind power to advanced artificial intelligence applications that enhance resource management, technology has the potential to play a pivotal role in mitigating climate impacts. As we embrace these innovations, collaboration between governments, businesses, researchers, and communities will be essential for scaling solutions effectively. By investing in climate technology now, we can create a sustainable future where economic growth aligns with environmental stewardship. The journey toward a greener planet is not just about adopting new technologies; it’s about rethinking our relationship with nature and committing to practices that prioritize sustainability at every level of society.
Read Ancient Algorithms: Roots of Modern Tech
Related Websites
- World Economic Forum – Insights into global efforts tackling climate change through innovation.
- International Energy Agency – Reports on renewable energy trends and technologies.
- NASA Climate Change – Information on climate science and technology solutions.
- Climate Tech VC – A resource dedicated to climate technology investments.
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change – Updates on international climate agreements and initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are some examples of climate technology?
- Examples include renewable energy sources (solar panels), electric vehicles (EVs), carbon capture systems, smart grids, precision agriculture tools, and AI-driven climate modeling software.
- How does technology help combat climate change?
- Technology helps by reducing greenhouse gas emissions through cleaner energy production methods, improving efficiency in resource usage, enabling data-driven decision-making for better environmental management, and facilitating innovative agricultural practices.
- What role does artificial intelligence play in addressing climate issues?
- AI enhances climate modeling accuracy, optimizes resource management across sectors (like agriculture), improves disaster preparedness through predictive analytics, and drives advancements in carbon capture technologies.
- Can individual actions make a difference in combating climate change?
- Yes! Individual actions such as reducing energy consumption at home, using public transportation or EVs when possible, supporting sustainable products or businesses, and advocating for policy changes contribute positively toward mitigating climate change.
- What is the importance of collaboration among stakeholders?
- Collaboration among governments, businesses, researchers, non-profits, and communities is crucial for sharing knowledge resources effectively; it enables scaling successful innovations quickly while fostering collective responsibility toward achieving sustainability goals.
By embracing innovative technologies alongside collaborative efforts across sectors globally—we can forge pathways toward resilient societies capable of thriving amidst environmental challenges ahead!

