Introduction
Thinking about going solar but not sure whether to choose an off-grid or on-grid system? You’re not alone! With the rising demand for renewable energy, homeowners and businesses are exploring solar power as a sustainable alternative. But which system is right for you? Let’s dive deep into the pros and cons of both off-grid and on-grid solar systems to help you make an informed decision.
What Is an On-Grid Solar System?

Predictive Maintenance for 3D Printing Machines Using IoT Sensors
An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied system, is connected to the local utility grid. This means that the electricity generated by your solar panels is either used immediately or sent back to the grid, depending on your energy consumption.
How Does an On-Grid System Work?
- Solar panels absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- Inverters transform the DC power from the panels into AC power for home use.
- Net metering allows excess electricity to be sent to the grid in exchange for credits.
- Grid dependency ensures you always have power, even when your panels aren’t producing energy.
Benefits of an On-Grid Solar System
- Lower upfront costs – No need for expensive batteries.
- Net metering – Sell excess electricity back to the utility company.
- Unlimited power supply – No need to worry about running out of stored energy.
- Easy maintenance – Fewer components mean less maintenance compared to off-grid systems.
Drawbacks of an On-Grid Solar System
- Grid dependence – No power during grid outages unless combined with battery storage.
- No energy autonomy – Subject to utility company policies and rate changes.
- Potential fees – Some utilities charge connection or demand fees.
What Is an Off-Grid Solar System?
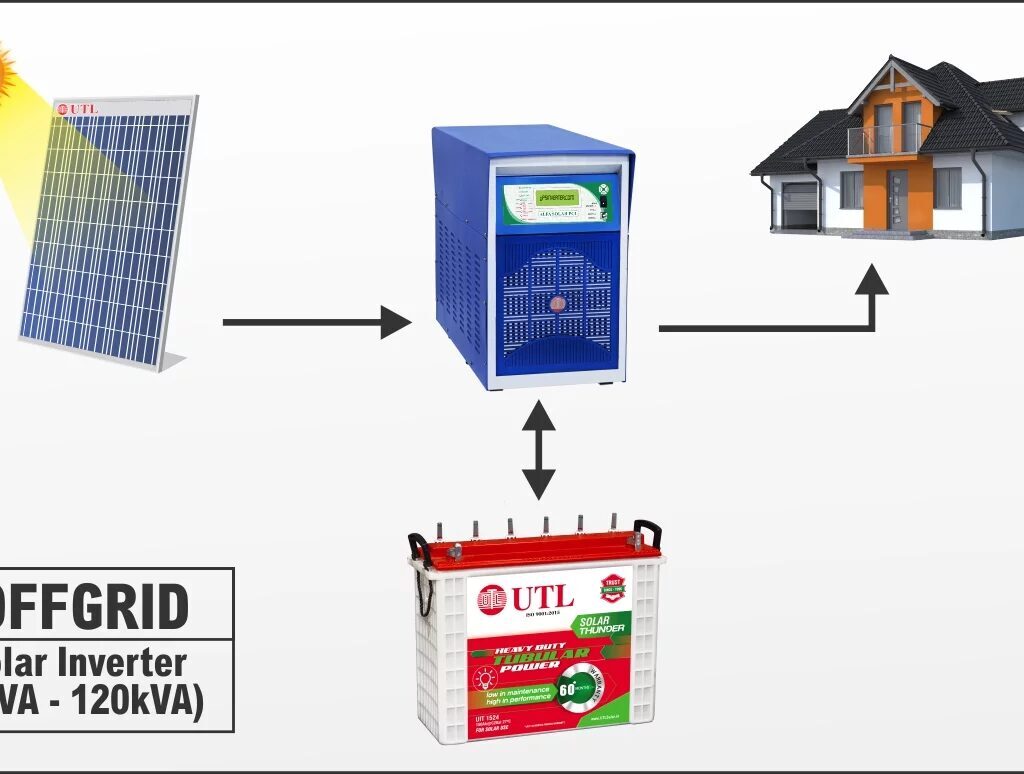
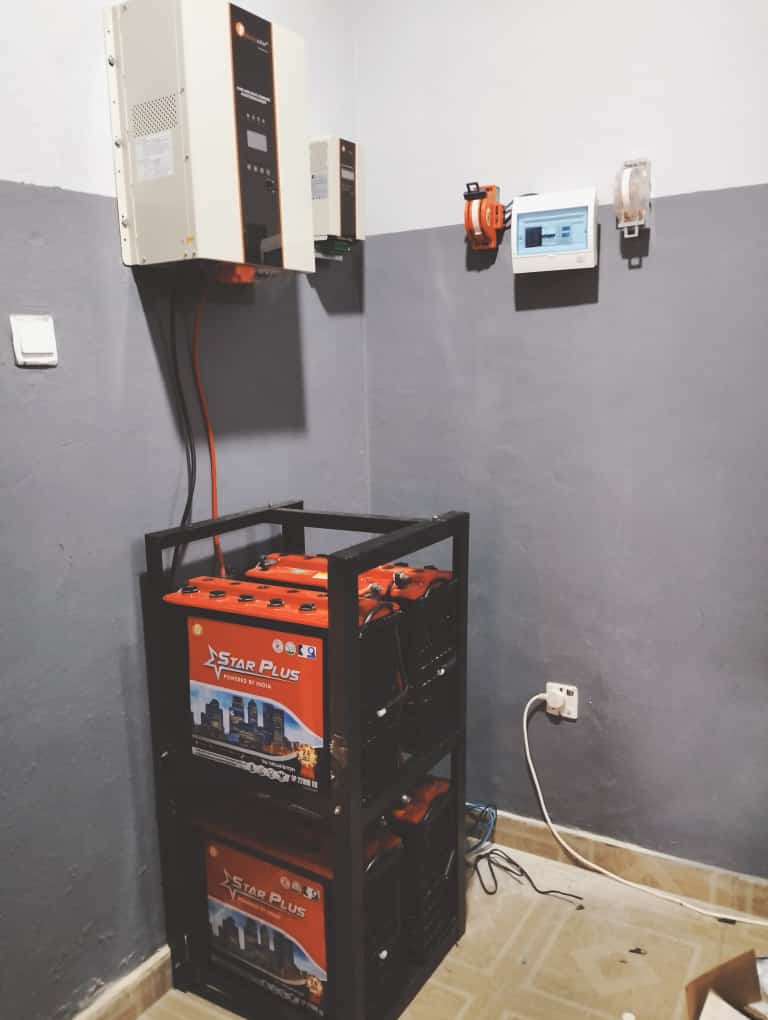
An off-grid solar system operates independently from the utility grid. It relies on solar panels and batteries to generate and store electricity for later use.
How Does an Off-Grid System Work?
- Solar panels generate electricity during the day.
- Charge controllers regulate power flow to batteries, preventing overcharging.
- Batteries store excess energy for nighttime or cloudy days.
- Inverters convert stored DC power into AC power for household appliances.
Benefits of an Off-Grid Solar System
- Energy independence – No reliance on the utility grid.
- Avoids blackouts – Power supply is unaffected by grid failures.
- No electricity bills – No monthly charges from the utility company.
- Sustainable living – Ideal for remote areas or eco-friendly lifestyles.
Drawbacks of an Off-Grid Solar System
- High initial costs – Batteries and additional components increase setup expenses.
- Limited energy storage – Batteries have a finite capacity and require careful management.
- More maintenance – Batteries degrade over time and need replacement.
- Energy use restrictions – Power must be carefully monitored to avoid running out.
Key Differences Between On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar Systems
| Feature | On-Grid System | Off-Grid System |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Connection | Connected to utility | Completely independent |
| Energy Storage | No storage, uses grid | Requires battery storage |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher upfront cost due to batteries |
| Reliability | Grid-dependent | Self-sustained power |
| Electricity Bills | May have charges | No monthly electricity bills |
| Power Outages | Affected by blackouts | Unaffected by grid failures |
Which Solar System Is Right for You?
Choose an On-Grid System If:
- You have reliable grid access.
- You want to lower your electricity bill rather than achieve full independence.
- You prefer lower upfront costs.
- You are comfortable with occasional power outages.
Choose an Off-Grid System If:
- You live in a remote location without grid access.
- You want complete energy independence.
- You can afford the higher initial investment.
- You are prepared to manage and maintain battery storage.
Hybrid Solar Systems: The Best of Both Worlds?

A hybrid solar system combines features of both on-grid and off-grid setups. It allows you to store energy in batteries while still being connected to the grid as a backup.
Benefits of a Hybrid Solar System
- Energy security – Batteries provide backup power during blackouts.
- Lower reliance on the grid – Use stored energy during peak rate hours.
- Flexible setup – Combines grid power with renewable energy efficiency.
However, hybrid systems can be more expensive due to battery costs, making them less common for budget-conscious homeowners.
The Cost Factor: Which Is More Affordable?
- On-grid systems are generally more affordable due to the absence of costly battery storage.
- Off-grid systems require high-capacity batteries, which significantly increase the overall cost.
- Hybrid systems strike a balance but tend to lean towards the pricier side due to dual functionality.
Government Incentives and Rebates
Depending on your location, you may qualify for tax credits, rebates, or other incentives that can help offset the costs of solar installation. Researching local programs can help you make a more cost-effective decision.
Environmental Impact: Which Is More Sustainable?
Both systems contribute to reducing carbon footprints, but off-grid systems may be more sustainable in remote areas by eliminating reliance on fossil fuel-powered grids.
Conclusion
Choosing between an on-grid and off-grid solar system depends on your energy needs, location, and budget. If you want affordability and convenience, go on-grid. If you seek independence and sustainability, go off-grid. Still undecided? A hybrid system might be the perfect middle ground.
FAQs
1. Can I switch from an on-grid to an off-grid system later?
Yes, but it requires additional investment in batteries and off-grid inverters.
2. What happens to excess power in an off-grid system?
It is either stored in batteries or wasted if storage is full, unless used for secondary applications like water heating.
3. How long do solar batteries last?
Most solar batteries last between 5 to 15 years, depending on the type and usage.
4. Is net metering available everywhere for on-grid systems?
No, net metering policies vary by location. Check with your utility provider.
5. Do off-grid systems require maintenance?
Yes, particularly the battery bank, which needs periodic checks and eventual replacement.