Have you ever stopped to think about the marvel of the internet? With a few clicks, you can connect with friends across the globe, access a library’s worth of information, or stream your favorite show. But how exactly does this invisible magic happen? Buckle up, because we’re diving deep into the fascinating world of how the internet works!
A Network of Networks
Imagine the internet as a massive highway system. Instead of cars, information travels in the form of tiny data packets. These packets are like individual suitcases containing pieces of information, like a website’s code or a video you’re watching.

Now, these highways aren’t straight roads leading from point A to point B. They’re a complex web of interconnected networks, like smaller roads and highways branching off from the main ones. Routers, acting as traffic controllers, decide which “road” (network) is the most efficient for each data packet to take to reach its destination.
Packing and Unpacking the Information
So, how does your information get packed into these data packets? When you type a web address (URL) into your browser, your computer translates it into a unique numerical address called an IP address. Think of it like a specific house number on a street – it tells the network exactly where to deliver the data packets.
These packets then travel through the network, hopping from router to router until they reach the destination – a web server. A web server is like a giant warehouse, storing all the information for a website. Once the packets arrive, the server unpacks them, reassembles the information, and sends it back to your computer. Your web browser then takes this information and displays it beautifully on your screen, allowing you to see the website or download the file.
The Language of the Internet
But how do all these devices communicate with each other? They all speak a common language called the TCP/IP protocol (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol). This protocol acts like a set of rules that ensures all devices on the internet can understand each other, regardless of their brand or operating system.
Think of it like traffic signals and lane markings on the highway. These standardized protocols allow data packets to travel smoothly and efficiently without any misunderstandings between different networks and devices.
Read Related Posts Like This…
- How to Identify and Solve High CPU Usage on A WordPress Site
- How to Fix an Overloaded WordPress Website
- How to Fix a WordPress Site with Malware
- How to Check Resources Usage
The Journey to Your Device
Now, how does this information actually reach your device? Here’s where your internet service provider (ISP) comes in. They’re like the bridge that connects your home or office to the vast internet highway. Your ISP provides you with a connection, often through a cable or fiber optic line.
This line connects to a modem in your home, which acts like a translator. It converts the digital signals from the ISP into a format your computer can understand and vice versa. Once the information is translated, it travels through your computer’s network card and onto your screen, bringing you the wonders of the internet.
Different Paths for Data
While we’ve focused on the traditional wired connection, the internet can also travel wirelessly. Wi-Fi networks, for example, use radio waves to transmit data packets between your device and a router. This allows you to connect to the internet without any physical cables, offering greater flexibility and mobility.
Similarly, cellular data networks allow you to access the internet on your smartphone or tablet even when you’re not connected to a Wi-Fi network. These networks use cell towers to transmit and receive data packets, keeping you connected on the go.
The Hidden World of Cloud Computing and content delivery networks (CDN)
The internet isn’t just about connecting devices. It’s also about storing and accessing vast amounts of data. Cloud computing allows us to store our information on remote servers accessed through the internet. This eliminates the need for physical storage devices and allows us to access our data from anywhere with an internet connection.
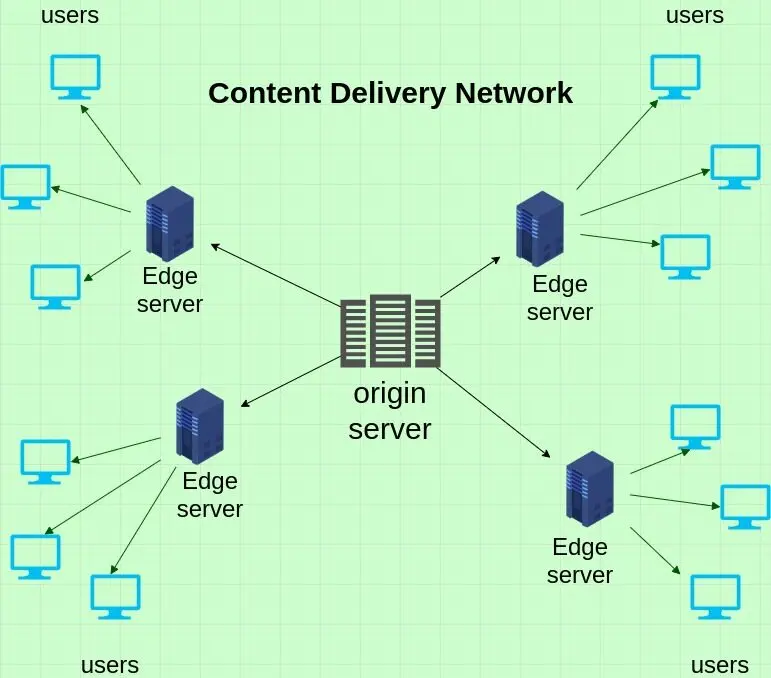
Content delivery networks (CDNs) play a crucial role in speeding up internet browsing. These networks store copies of frequently accessed data (like website content or videos) on servers around the world. When you request this information, it’s delivered from the closest server, significantly reducing loading times.
Maintaining the Flow
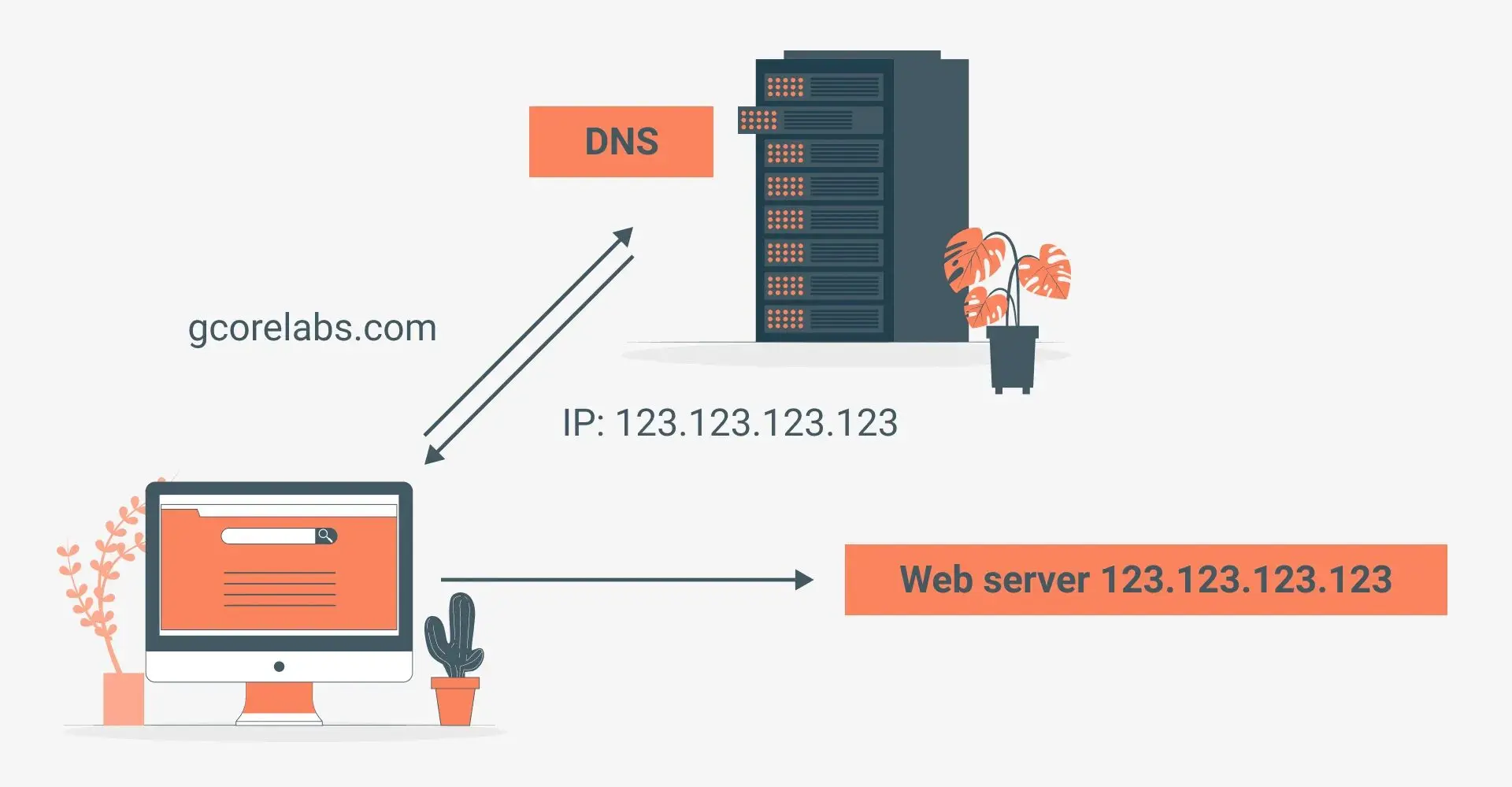
Imagine if you had to remember long strings of numbers to access websites instead of user-friendly web addresses. That’s where the Domain Name System (DNS) comes in. DNS servers act like giant phone books for the internet, translating human-readable domain names trendybitz.net into the corresponding IP addresses that computers can understand. This allows you to simply type in a web address and access the desired website without needing to memorize complex numerical codes.
Behind the scenes, a vast network of cables, satellites, and undersea fiber optic lines make up the internet’s backbone. These physical infrastructures carry the data packets across vast distances, ensuring smooth information flow across the globe.
The Future of the Internet: A Glimpse Ahead
The internet is constantly evolving, and the future holds exciting possibilities. The Internet of Things (IoT) envisions a world where everyday objects are connected to the internet, allowing them to collect and share data. Imagine your refrigerator automatically ordering groceries when it runs low or your thermostat adjusting based on your preferences.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is also playing an increasingly important role in the internet’s future. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to personalize your online experience, recommend content you might be interested in, or even power chatbots that can answer your questions.

Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies are blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds. VR allows you to immerse yourself in simulated environments, while AR overlays digital information onto the real world. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize how we learn, work, and interact with the world around us.
Challenges and Considerations
While the internet offers immense benefits, it also presents certain challenges. Net neutrality, the principle that all internet traffic should be treated equally, is a critical issue. Without it, internet service providers could potentially prioritize certain types of content or throttle speeds, impacting the user experience.
The digital divide refers to the gap between those who have access to the internet and those who don’t. This can limit access to information, education, and economic opportunities. Bridging this gap is crucial to ensure everyone benefits from the digital age.
Cybersecurity is another major concern. As we become increasingly reliant on the internet, protecting our data and online identities becomes paramount. Implementing robust security measures and practicing safe online habits are essential to navigate the digital world safely.
Conclusion
The internet has transformed the way we live, work, and communicate. From connecting with loved ones to accessing information and entertainment, the internet offers a world of possibilities at our fingertips. By understanding how the internet works, we can appreciate its complexity and leverage its power to its fullest potential.
Unique FAQs
- What if I don’t have a wired connection? Can I still access the internet?
Absolutely! Wireless networks and cellular data allow you to access the internet without cables. Wi-Fi networks provide internet access within a specific range, while cellular data allows you to connect on the go using cell towers.
- Why does my internet sometimes feel slow?
Several factors can contribute to slow internet speeds. These include overloaded networks, outdated equipment, or limitations set by your internet service provider.
- What is the difference between the internet and the World Wide Web?
The internet is the vast infrastructure that connects devices and allows data to flow. The World Wide Web (WWW) is a service built on top of the internet that allows us to access information through web pages and websites.
- How can I protect myself online?
There are several ways to stay safe online. Use strong and unique passwords, be cautious about clicking on suspicious links or downloading files, and keep your software and devices updated with the latest security patches.
- What is the future of the internet?
The future of the internet is full of possibilities. We can expect advancements in areas like the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and virtual reality, further blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds.
Quiz Test Questions: How the Internet Works (Undergraduate Level)
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
- What is the primary function of the Domain Name System (DNS)?
- a) To store and manage website content
- b) To translate domain names (like trendybitz.net) into IP addresses (like 142.250.184.196)
- c) To encrypt data transmission over the internet
- d) To control access to specific websites
- What is the role of a router in an internet connection?
- a) To display webpages on your computer screen
- b) To direct data packets to their intended destination on the internet
- c) To connect multiple devices to a single network
- d) To search for information on the internet
- How does the internet differentiate between different devices connected to it?
- a) By username and password
- b) By unique Media Access Control (MAC) addresses
- c) By the operating system of the device
- d) By the type of web browser used
- What is the difference between a web server and a web browser?
- a) There is no difference, they are the same thing.
- b) A web server stores website content and delivers it to browsers upon request.
- c) A web browser displays webpages and allows users to interact with them.
- d) A web server is for static content, while a web browser is for dynamic content.
- What is the primary function of the TCP/IP protocol suite?
- a) To compress data for faster transmission
- b) To define a set of rules for communication over the internet
- c) To provide security for online transactions
- d) To translate between different languages on the internet
- What is the term for the path data takes when traveling across the internet?
- a) Information Highway
- b) Digital Pathway
- c) Data Stream
- d) Packet Switched Network
- What is the difference between a wired and wireless internet connection?
- a) Wired connections are faster and more reliable, while wireless connections are slower and less secure.
- b) Wireless connections are faster and more reliable, while wired connections are slower and less secure.
- c) Wired connections use cables, while wireless connections use radio waves.
- d) Wired connections are for personal computers, while wireless connections are for mobile devices.
- What is the role of a search engine like Google or Bing?
- a) To host and display website content
- b) To organize and index websites to allow users to find relevant information
- c) To provide security for online transactions d) To manage email accounts
- What is the term for a website that provides false or misleading information?
- a) Phishing Site
- b) Spam Website
- c) Clickbait Site
- d) Spoof Website
- What is the concept of “Net Neutrality” about?
- a) The freedom to access any website on the internet without restrictions.
- b) The prioritization of certain types of internet traffic over others.
- c) The encryption of all data transmitted over the internet.
- d) The regulation of online content.