Introduction
Education is a cornerstone of human progress, shaping societies and empowering individuals. But how did teaching and learning evolve into the complex systems we know today? From ancient oral traditions to digital classrooms, the history of education reveals a fascinating journey through time. This article explores the milestones that have defined education’s evolution, shedding light on how past practices influence contemporary learning.
The Origins of Education
Oral Traditions and Early Knowledge Sharing
Before the advent of writing, knowledge was passed down orally from one generation to the next. Storytelling, songs, and rituals were central to teaching cultural values and practical skills.
Education in Ancient Civilizations
In ancient Mesopotamia, Egypt, and China, education was formalized to train scribes, priests, and administrators. Writing systems such as cuneiform and hieroglyphs played a critical role in preserving and transmitting knowledge.
Education in the Classical Era
Ancient Greece: The Birthplace of Philosophy
In Greece, education focused on developing intellectual and physical abilities. Philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle emphasized critical thinking and ethical living, laying the foundation for modern pedagogy.
Roman Education: Practical Knowledge for Governance
The Romans emphasized practical skills such as rhetoric, law, and military tactics. Schools catered mainly to elites, with teachers often being Greek slaves or freedmen.
The Middle Ages: Religious Dominance in Education
The Rise of Monastic Schools
During the medieval period, monasteries became centers of learning. Monks preserved classical texts and provided religious and basic secular education.
The Role of Islamic Scholarship
The Islamic Golden Age (8th–13th centuries) saw the establishment of madrasas and a focus on science, medicine, and philosophy. Renowned scholars like Al-Farabi and Avicenna contributed significantly to global knowledge.
Renaissance and Humanism
Revival of Classical Knowledge
The Renaissance (14th–17th centuries) reignited interest in classical education. Schools emphasized liberal arts, including grammar, rhetoric, and logic, aiming to cultivate well-rounded individuals.
Printing Revolution and Accessibility
The invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century revolutionized education. Books became more affordable, spreading knowledge beyond elite circles.
The Industrial Revolution and Mass Education
Public School Systems
The 19th century witnessed the rise of public education, driven by industrial needs. Governments introduced compulsory schooling to create literate and skilled workforces.
Educational Philosophies
Thinkers like John Dewey advocated experiential learning, emphasizing the importance of critical thinking and democracy in education.
The 20th Century: Globalization of Education
Expansion of Higher Education
Universities proliferated globally, offering diverse disciplines and fostering research. Education became increasingly accessible, thanks to scholarships and public funding.
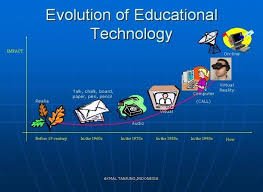
Technological Advances
The introduction of audiovisual tools, computers, and later the internet transformed traditional classrooms into dynamic learning environments.
Education in the Digital Age
Online Learning and Virtual Classrooms
Platforms like Coursera and Khan Academy make high-quality education accessible worldwide. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote learning technologies.
Personalized Learning with AI
Artificial intelligence enables adaptive learning systems that cater to individual student needs, enhancing engagement and outcomes.
Themes and Patterns in Educational Evolution
Inclusivity and Accessibility
From exclusive systems serving elites to universal education models, the trend toward inclusivity is a hallmark of education’s evolution.
Integration of Technology
Technology has consistently expanded the reach and scope of education, from printing presses to AI-driven tools.
Lifelong Learning
The growing recognition of education as a lifelong journey reflects shifting societal and economic demands.
Check; The Art of Communication in Love: Speaking the Language of the Heart
Challenges and Opportunities in Education Today
Bridging the Digital Divide
While technology has democratized learning, access disparities persist, particularly in developing regions.
Balancing Tradition and Innovation
Modern educators grapple with incorporating innovative methods while preserving cultural and historical knowledge.
Fostering Critical Thinking
In an era of information overload, teaching critical evaluation skills is more vital than ever.
Significant Figures in the History of Education
Confucius (551–479 BCE)
A Chinese philosopher who emphasized moral education and lifelong learning.
Maria Montessori (1870–1952)
An Italian educator who developed child-centered teaching methods, fostering independence and creativity.
Paulo Freire (1921–1997)
A Brazilian educator who championed critical pedagogy, empowering marginalized communities through education.
The Role of Cultural Context in Education
Western vs. Eastern Educational Traditions
Western systems often emphasize individuality and critical thinking, while Eastern traditions value discipline and collective well-being.
Indigenous Knowledge Systems
Indigenous communities worldwide have rich educational traditions rooted in environmental stewardship and oral histories.
Personal Reflection on Education’s Evolution
Reflecting on education’s history highlights its dynamic nature, shaped by societal needs and cultural values. It’s inspiring to see how education adapts to challenges, from the Renaissance revival of classical texts to today’s embrace of digital tools. By understanding this evolution, we can appreciate the diversity of teaching methods and their impact on learners worldwide.
Conclusion
The history of education is a testament to humanity’s pursuit of knowledge and progress. From oral traditions to AI-driven platforms, each stage of this journey has built upon the last, creating an ever-expanding legacy of learning. By honoring the past and embracing innovation, we can shape an educational future that empowers everyone to thrive.
FAQs
1. What is the significance of education in ancient civilizations?
Education in ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia and Egypt focused on training scribes and preserving knowledge, laying foundations for future systems.
2. How did the Renaissance influence education?
The Renaissance revived classical knowledge and emphasized liberal arts, fostering creativity and critical thinking in education.
3. What role did the Industrial Revolution play in education?
The Industrial Revolution spurred public education systems to meet the demands of a literate and skilled workforce.
4. How has technology transformed education?
From printing presses to online learning platforms, technology has consistently expanded education’s reach and accessibility.
5. What are the key challenges in modern education?
Challenges include bridging the digital divide, balancing tradition with innovation, and fostering critical thinking in an age of information overload.