The animal kingdom is a tapestry woven with vibrant colors, diverse species, and some truly extraordinary abilities. We’ve all witnessed the cheetah’s lightning-fast sprints or the awe-inspiring migrations of birds, but these are just the tip of the iceberg. Dolphins navigate murky depths with sonar-like precision, while some creatures illuminate the ocean floor with an ethereal glow. Even stranger, certain animals possess regenerative powers that would make comic book superheroes jealous. Buckle up, animal enthusiasts, because we’re diving deep into the fascinating world of these mind-blowing animal abilities!

Navigating the Dark: The Wonders of Echolocation
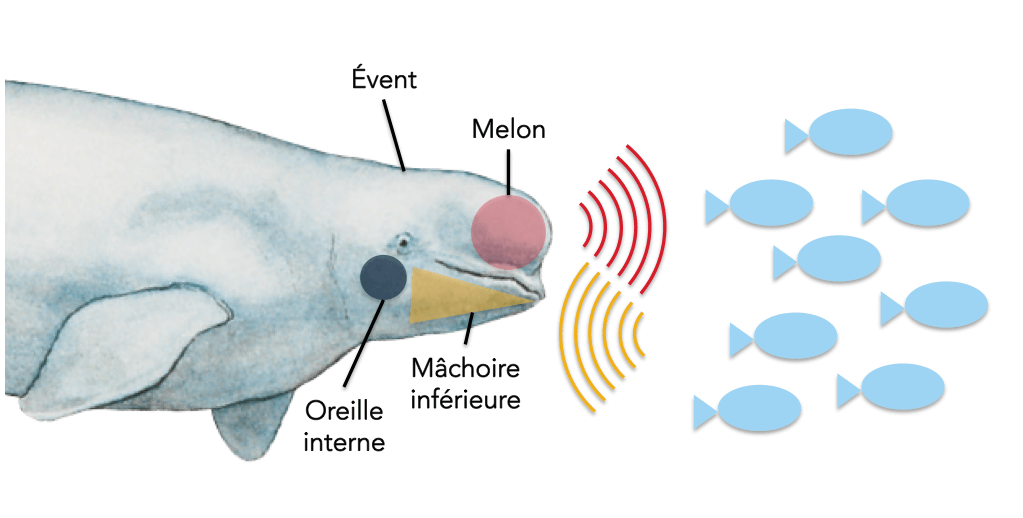
Imagine driving blindfolded through a bustling city. Sounds like an impossible feat, right? Well, for dolphins, whales, and even some bats, this is child’s play. These incredible creatures utilize echolocation, a biological sonar system, to perceive their surroundings. They emit high-frequency clicks or whistles that bounce off objects and return, creating an auditory map of their environment. By analyzing the echoes, they can pinpoint the location, size, and even shape of objects, allowing them to hunt, navigate, and avoid obstacles with remarkable accuracy. Think of it as a built-in GPS that works even in complete darkness or murky water!
Glowing Giants: Unveiling the Mystery of Bioluminescence
Have you ever seen the mesmerizing spectacle of fireflies dancing on a summer night? This captivating display is just one example of bioluminescence, the production of light by living organisms. Deep within the ocean’s abyss, a dazzling array of creatures, from jellyfish to anglerfish, illuminate the darkness. But why would an animal invest energy in producing its own light source? The reasons are as diverse as the creatures themselves. Some bioluminescent animals use light to attract prey, while others employ it as a dazzling defense mechanism, momentarily stunning predators. Still others utilize bioluminescence for communication, sending silent signals to potential mates or fellow members of their species.
Regeneration Revolution: Animals That Cheat Death (Almost)
Have you ever wished you could rewind time and heal a nasty scrape in a flash? Well, some animals possess the remarkable ability to regenerate lost limbs or even entire body parts! The axolotl, a cute, salamander-like creature found in Mexico, is the king of regeneration. Axolotls can regrow limbs, tails, jaws, even portions of their brains and hearts! While this ability diminishes as they mature, it’s still a phenomenal feat. Flatworms can split themselves in two, essentially becoming clones, and some starfish can regenerate entire arms if one is severed. Scientists are actively researching these incredible regenerative abilities, hoping to unlock the secrets that could revolutionize human medicine.

Beyond the Obvious: A Peek at Lesser-Known Animal Talents
The animal kingdom is overflowing with hidden talents that go beyond the usual suspects. Did you know that electric eels can generate enough electricity to stun a horse? Talk about a shocking surprise! Archerfish have incredible aim and can spit jets of water to knock insects off plants for an easy meal. Dung beetles possess a remarkable sense of smell and can navigate by the Milky Way! Even the humble honeybee displays impressive feats of memory, remembering the location of flowers miles away from the hive.
Masters of Mimicry: The Art of Deception in the Wild
Nature is full of talented impersonators, and some animals have taken mimicry to an art form. The lyrebird, a songbird native to Australia, is a champion mimic. It can flawlessly replicate the calls of other birds, even chainsaws and car alarms! This ability allows lyrebirds to attract mates and defend their territory. Chameleons, renowned for their color-changing abilities, aren’t just masters of disguise; they also use their rapid color shifts for communication and temperature regulation. Mimicry is a powerful survival tool, allowing animals to blend in, deceive predators, and even attract mates.

Masters of the Senses: Animals with Superhuman Perception
Imagine being able to hear a pin drop from a mile away or see colors invisible to the human eye. For some animals, this is everyday life. Owls have exceptional hearing, allowing them to pinpoint the location of prey even in total darkness. Sharks possess an extraordinary sense of smell, capable of detecting a single drop of blood in a million gallons of water! Snakes can perceive infrared radiation through special pits on their heads, allowing them to “see” heat signatures and hunt warm-blooded prey even at night. These incredible sensory abilities give animals a significant edge in the competitive world of survival.
The Power of Electroreception: Feeling the Electric Fields
While most of us rely on sight, sound, and smell to navigate the world, some animals possess a unique superpower: electroreception. This ability allows them to sense weak electrical fields generated by living organisms or even the Earth’s magnetic field. Imagine being able to feel the electrical impulses of a beating heart or the subtle electrical currents running through water! For certain creatures, electroreception is a vital tool for hunting, communication, and even avoiding predators.
Sharks are masters of electroreception. Tiny pores located around their snouts can detect the faint electrical fields emitted by the muscular contractions of prey animals. This allows them to locate hidden fish buried in the sand or navigate murky waters with pinpoint accuracy. Electric eels, ironically, utilize electroreception not just to generate their own electrical fields but also to sense the electrical discharges of other electric eels, helping them avoid each other. Even some surprisingly ordinary creatures, like platypuses, possess electroreception bills that allow them to detect the electrical fields of shrimp and other small prey in murky water.
Chemical Communication: The Silent Language of Scents
Sight and sound aren’t the only ways animals communicate. Many creatures rely on a complex language of scents, utilizing their keen sense of smell to send messages to each other. Dogs, of course, are famous for their olfactory prowess. They can detect a vast array of scents, allowing them to track prey, identify other animals, and even recognize their human companions. Elephants communicate through a complex system of chemical signals released through glands behind their temples. These messages can convey information about danger, food sources, or even social hierarchy. Snakes use their forked tongues to “smell the air,” collecting scent molecules that they then transfer to a special organ in the roof of their mouth for analysis. This allows them to track prey, locate mates, and identify potential threats.
Masters of Deception: The Art of Camouflage
Mimicry isn’t the only trick animals have up their sleeves when it comes to disappearing in plain sight. Camouflage allows animals to blend seamlessly into their surroundings, becoming virtually invisible to predators. Chameleons may be the most famous example, but countless creatures utilize camouflage for survival. Stick insects perfectly resemble twigs, while flounder fish can alter their skin color and pattern to match the seabed. Polar bears blend in with snowy landscapes, while owls have mottled feathers that camouflage them against tree bark. Camouflage isn’t just about color; some animals have evolved unique body shapes that mimic their surroundings. For instance, leaf insects have flattened bodies and protruding veins that make them look remarkably like leaves.
Super Sticky Situations: The Power of Adhesion
Imagine being able to defy gravity and cling to any surface, even upside down! For some creatures, this is a reality. Geckos possess microscopic hairs on their feet that create a powerful adhesive force, allowing them to scale walls and ceilings with ease. Spiders utilize silk pads on their feet to adhere to smooth surfaces, while some insects secrete a sticky glue that helps them cling to leaves and other objects. These adhesive abilities give these animals a significant advantage, allowing them to access food sources, escape predators, and even lay their eggs in precarious locations.
Masters of Construction: The Architects of the Animal Kingdom
While humans are known for their impressive feats of engineering, some animals are natural-born architects. Beavers are master builders, constructing elaborate dams and lodges using logs, branches, and mud. Termites create towering mounds that can reach several meters high, featuring intricate ventilation and temperature control systems. Birds weave intricate nests from twigs, leaves, and even hair, providing a safe haven for their young. Social insects, such as ants and bees, construct complex colonies with dedicated chambers for food storage, raising young, and housing the queen. These incredible feats of construction showcase the ingenuity and problem-solving skills of the animal kingdom.
Conclusion: A Celebration of Nature’s Wonders
The animal kingdom is a never-ending source of wonder and amazement. From the echolocation of dolphins to the bioluminescent glow of deep-sea creatures, nature has equipped its inhabitants with an astonishing array of abilities. These mind-blowing feats not only allow animals to survive in a challenging world but also inspire scientific discovery and innovation. As we continue to learn more about these incredible creatures, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of the natural world.
Read Also
- Natural Remedies for Everyday Health Issues
- Get Fit From Home: The Beginner’s Guide to Building a Home Gym on a Budget
- “Perfection” by R.L. Mathewson.
- The Ultimate Guide to Building Your Own PC
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Mind-Blowing Animal Abilities
Here are some of the most common questions people ask about the extraordinary abilities of animals:
1. Can any animals heal themselves like the axolotl?
While the axolotl’s regenerative powers are truly remarkable, some other animals exhibit impressive healing abilities. Starfish can regenerate lost arms, and flatworms can even split themselves in two, essentially becoming clones. Scientists are actively studying these regenerative processes in hopes of unlocking treatments for human injuries and diseases.
2. Are there any bioluminescent animals on land?
Yes! Fireflies are the most well-known example of land-dwelling bioluminescent creatures. They use their light for communication, attracting mates and deterring predators. Some fungi and even millipedes also possess bioluminescent properties.
3. How do animals use echolocation navigate such complex environments?
Echolocation is a highly sophisticated skill. Dolphins and bats emit clicks or whistles at high frequencies. By analyzing the returning echoes, they can determine the size, shape, and distance of objects in their environment. This allows them to navigate through intricate underwater caves or dense forests with remarkable precision.
4. Are there any dangers associated with bioluminescence?
For some deep-sea creatures, bioluminescence can be a double-edged sword. While it attracts prey, it can also attract predators. Some anglerfish use bioluminescent lures to attract unsuspecting prey, while others use bioluminescent flashes to momentarily blind predators and create an escape opportunity.
5. Can humans ever develop any of these animal abilities?
While we may not be able to grow back limbs or navigate by echolocation, scientific advancements inspired by animal abilities are already happening. Researchers are developing prosthetic limbs with improved functionality and control inspired by the dexterity of animal limbs. Biomimicry, the imitation of nature’s designs, is also leading to innovations in areas like materials science and robotics. The future holds exciting possibilities as we continue to learn from the incredible abilities of the animal kingdom.

