How Your Data is Exploited
Introduction
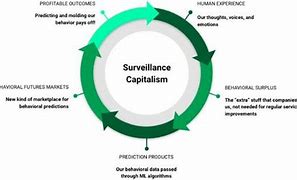
In today’s digital world, it seems like everything we do online is being watched. From the moment we log in to our social media accounts to the time we shop online, our actions are meticulously tracked and analyzed. This phenomenon is known as surveillance capitalism, a term coined by Shoshana Zuboff. It refers to the commodification of personal data by corporations that seek to predict and influence our behavior for profit. But what does this mean for us as individuals? Are we merely products in a vast data marketplace? In this article, we will delve into the unsettling truths about surveillance capitalism, exploring how our data is exploited, who benefits from it, and what we can do to reclaim our privacy.
What is Surveillance Capitalism?
Surveillance capitalism is a new economic model that takes advantage of personal data collected through various digital platforms. Companies like Google, Facebook, and Amazon gather extensive information about users’ behaviors, preferences, and interactions. This data is then used to create detailed profiles that help businesses predict future behaviors and tailor their marketing strategies accordingly. Essentially, it transforms our personal experiences into raw material for profit.

The Birth of Surveillance Capitalism
The concept of surveillance capitalism emerged in the early 2000s when tech companies began to realize the value of behavioral data. With the rise of social media and smartphones, user-generated content became a goldmine for these corporations. They quickly learned that by collecting more data than necessary for their services, they could sell predictions about user behavior to advertisers and other businesses.
The Key Players in Surveillance Capitalism
Big Tech Companies
The primary players in surveillance capitalism are tech giants like Google, Facebook (now Meta), Amazon, and Apple. These companies have built empires on the back of user data. They offer “free” services but monetize them by selling access to their users’ information.
Data Brokers
Another significant player in this ecosystem is data brokers—companies that collect information from various sources and sell it to other businesses. They aggregate data from public records, online activity, and even offline transactions to create comprehensive profiles on individuals.
Governments
While private companies are often at the forefront of surveillance capitalism, governments also play a crucial role. Many governments partner with tech companies to access user data for various purposes, including national security and law enforcement.
How Your Data is Collected
Online Activity Tracking
Every time you browse the web or use an app, your actions are tracked through cookies and other tracking technologies. These tools collect information about your preferences, interests, and behaviors.
Social Media Engagement
Social media platforms are particularly adept at gathering user data. Every post you like, comment on, or share provides valuable insights into your personality and preferences.
IoT Devices
The rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices adds another layer to data collection. Smart home devices like thermostats and speakers continuously gather information about your habits and routines.
The Implications of Surveillance Capitalism
Erosion of Privacy
One of the most alarming consequences of surveillance capitalism is the erosion of privacy. Users often unknowingly consent to extensive data collection practices that compromise their personal information.
Behavioral Manipulation
Surveillance capitalism doesn’t just stop at collecting data; it uses that information to manipulate behavior. Companies employ sophisticated algorithms to target users with personalized ads designed to influence their purchasing decisions.
Economic Inequality
Surveillance capitalism can exacerbate economic inequality by creating a divide between those who can afford privacy protections and those who cannot. Wealthier individuals may have access to tools that safeguard their data while others remain vulnerable.
Real-World Examples of Surveillance Capitalism

Cambridge Analytica Scandal
One of the most infamous examples of surveillance capitalism occurred during the 2016 U.S. presidential election when Cambridge Analytica harvested personal data from millions of Facebook users without their consent. This data was used to create targeted political ads aimed at influencing voter behavior.
Health Data Exploitation
Health insurance companies are increasingly turning to surveillance capitalism by purchasing health-related data from various sources. This information helps them assess risks and determine premiums but raises ethical concerns about patient privacy.
How Companies Benefit from Your Data
Predictive Analytics
Companies leverage predictive analytics to forecast user behavior based on historical data. This allows them to tailor marketing strategies effectively and maximize profits.
Targeted Advertising
By analyzing user behavior, companies can deliver highly targeted advertisements that resonate with specific audiences. This not only increases conversion rates but also enhances customer satisfaction by providing relevant offers.
The Ethical Concerns Surrounding Surveillance Capitalism
Lack of Transparency
One major ethical concern is the lack of transparency in how companies collect and use personal data. Many users are unaware of the extent to which their information is being harvested or how it will be utilized.
Consent Issues
While many platforms require users to agree to terms and conditions before using their services, these agreements are often lengthy and complex. As a result, users may unknowingly consent to invasive data collection practices.
What Can You Do About It?
Educate Yourself
Understanding how surveillance capitalism operates is the first step toward protecting yourself. Stay informed about privacy policies and be wary of sharing personal information online.
Use Privacy Tools
Consider using privacy-focused tools such as VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), ad blockers, or browser extensions designed to enhance your online security.
Limit Data Sharing
Be mindful of what you share on social media platforms and consider adjusting your privacy settings to limit access to your personal information.
The Future of Surveillance Capitalism
As technology continues to evolve, so too will surveillance capitalism. With advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, companies will likely find even more sophisticated ways to analyze user behavior. This raises questions about how society will address these challenges moving forward.
Regulation Efforts
In response to growing concerns about privacy violations, governments worldwide are beginning to implement regulations aimed at curbing surveillance capitalism practices. The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is one such example that seeks to give individuals more control over their personal information.
Read this: How to Know the Best Cryptocurrency Exchanges for your Investment
Conclusion: Reclaiming Your Privacy
Surveillance capitalism represents a profound shift in how personal data is collected and exploited for profit. While it offers businesses valuable insights into consumer behavior, it poses significant risks to individual privacy and autonomy. By understanding how your data is collected and used, you can take steps toward reclaiming your privacy in an increasingly surveilled world. As consumers become more aware of these issues, they can demand greater transparency from companies and advocate for stronger regulations that protect their rights in this new digital landscape.
Meta Description
Discover the unsettling truth about surveillance capitalism and how your personal data is exploited for profit. Learn about its implications, key players, and what you can do.
FAQs
- What is surveillance capitalism?
- Surveillance capitalism refers to the commodification of personal data by corporations that track user behavior for profit without explicit consent or compensation.
- How do companies collect my data?
- Companies collect data through various means such as online activity tracking (cookies), social media engagement, and IoT devices.
- What are some real-world examples of surveillance capitalism?
- Notable examples include the Cambridge Analytica scandal during the 2016 U.S. presidential election and health insurance companies purchasing health-related data.
- What can I do to protect my privacy?
- Educate yourself about privacy policies, use privacy tools like VPNs or ad blockers, and limit what you share on social media.
- Are there regulations against surveillance capitalism?
- Yes, some regulations like the GDPR aim to give individuals more control over their personal information and limit invasive practices by companies.

