
The World Unseen: Unveiling the Science in Our Daily Lives
Have you ever gazed at a breathtaking sunset, awestruck by the fiery hues of orange and red streaking across the canvas of the sky? Or perhaps you’ve pondered the seemingly effortless way a bird soars through the air, defying gravity with such grace. These everyday experiences, often taken for granted, hold within them a universe of scientific principles waiting to be unraveled.
This article embarks on a journey to demystify some of the most common phenomena we encounter every day. By delving into the fascinating world of science, we’ll gain a deeper understanding of the “why” behind the “wow” in our daily lives.

The Wizardry of Color: Why We See a Rainbow After the Rain
Imagine a world devoid of color, a monotonous landscape painted in shades of grey. Thankfully, our reality is a vibrant tapestry woven from a spectrum of colors. But what exactly is color, and why do objects appear differently colored?
The answer lies in the fascinating dance between light and matter. Sunlight, which appears white to the naked eye, is actually composed of a rainbow of colors, each with a distinct wavelength. When light interacts with an object, some wavelengths are absorbed, while others are reflected. The reflected wavelengths are what our eyes perceive as color.
For instance, a red apple absorbs all other wavelengths of light except red, which it reflects back to our eyes, registering as the color red. The next time you witness a rainbow after a downpour, remember it’s not magic, but the clever manipulation of light by water droplets in the atmosphere, separating the various wavelengths and creating a breathtaking spectacle.
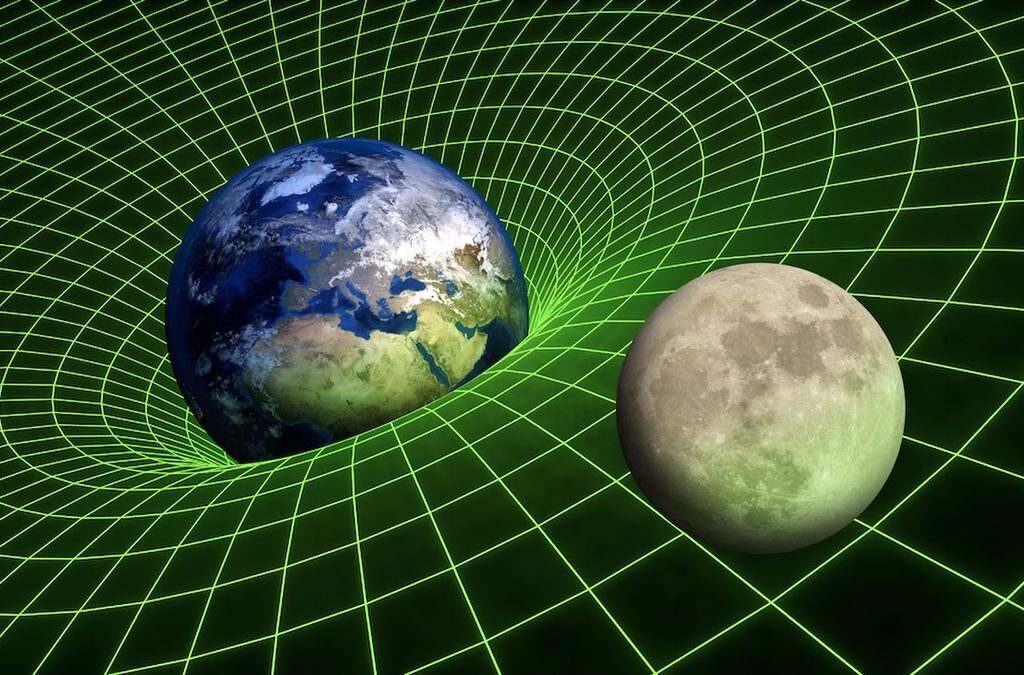
The Invisible Force: Gravity’s Hold on Us
Ever wondered why objects fall down when dropped? It’s not because the Earth is flat and things simply “fall off” the edge. The answer lies in a fundamental force of nature called gravity.
Gravity, discovered by the brilliant scientist Isaac Newton, is an invisible force that attracts any two objects with mass towards each other. The greater the mass of an object, the stronger its gravitational pull. This explains why we stay firmly planted on Earth’s surface – the Earth’s immense mass exerts a strong gravitational pull on us.
The concept of gravity extends far beyond our everyday experiences. It governs the motion of planets around the sun, keeps satellites in orbit, and even plays a role in the formation of stars and galaxies.

Beyond the Basics: Exploring Other Fascinating Phenomena
Our exploration of science in everyday life doesn’t end with color and gravity. Let’s delve into a few more captivating examples:
- The Science of Sound: Why does thunder rumble and a violin create a melodious tune? Sound is simply vibrations travelling through a medium, like air or water. The frequency of these vibrations determines the pitch we hear, while the amplitude determines the volume.
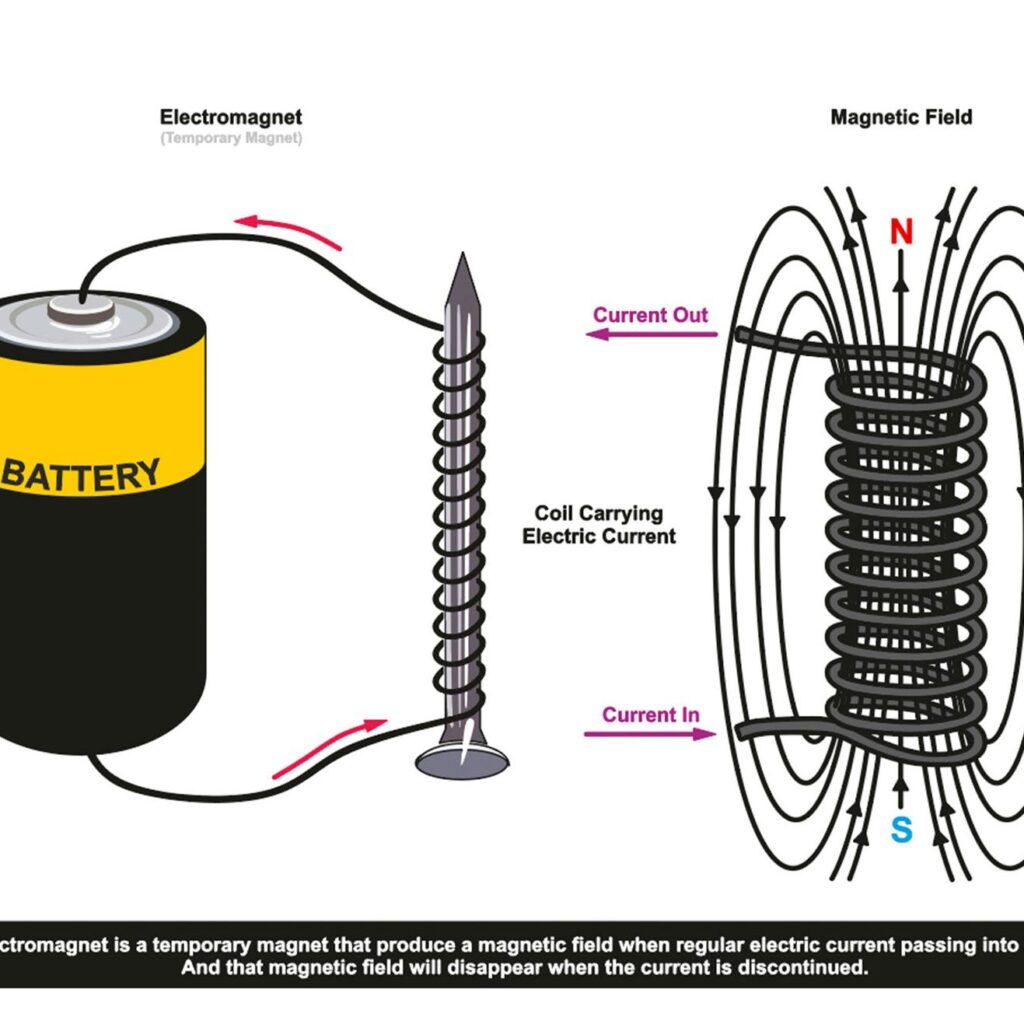
- The Mystery of Magnets: Have you ever been captivated by the seemingly magical attraction between magnets? Tiny regions within a magnet called domains align in a specific way, creating a magnetic field that attracts or repels other magnets with opposing or similar alignments.
- The Magic of Electricity: From powering our homes to allowing us to communicate instantly, electricity plays a vital role in our modern world. Electricity is the flow of charged particles, typically electrons, through a conductor. This flow of electrons powers countless devices and applications.
By understanding the scientific principles behind these everyday phenomena, we not only gain a deeper appreciation for the world around us, but also unlock the potential to innovate and create new technologies that shape our future.
Beyond the Obvious: The Interconnectedness of Science
It’s important to remember that science isn’t a collection of isolated facts. Different scientific disciplines are intricately linked. For example, the science of light (optics) plays a crucial role in our understanding of how we see color. Similarly, the principles of electricity underpin the operation of many devices that utilize sound or magnetism.
This interconnectedness is a testament to the beautiful unity and elegance of the natural world. By appreciating these connections, we gain a more holistic understanding of the universe we inhabit.
Conclusion: A World of Wonder Awaits
The world around us is brimming with scientific marvels waiting to be discovered. From the breathtaking colors of a sunset to the invisible force of gravity keeping us grounded, everyday experiences hold the key to unlocking a universe of knowledge. As we delve deeper into the science behind these phenomena, we not only gain a deeper appreciation for the world, but also fuel our curiosity and inspire us to explore the boundless possibilities that science offers. So, the next time you encounter
Read Similar Posts
- Myth and Truths: Does Half-Open Valve Save Fuel?
- The Science of Learning: Exploring Effective Techniques for Knowledge Retention
- Unlocking Creativity: Exploring Techniques to Spark New Ideas and Approaches
- Everyday Habits Hijacking Your Happiness: Unrecognized Threats to Mental Wellbeing
FAQs: Demystifying Everyday Science
Here are some frequently asked questions to quench your thirst for scientific knowledge:
FAQ 1: Why does the sky appear blue?
The answer lies in a phenomenon called Rayleigh scattering. Sunlight, containing a spectrum of colors, interacts with air molecules. By these molecules, blue light, which has a shorter wavelength, is scattered more effectively, reaching our eyes from all directions and painting the sky blue.
FAQ 2: Can we escape Earth’s gravity?
Earth’s escape velocity, which is the minimum speed needed for an object to break free from Earth’s gravitational pull, must be overcome. Rockets achieve this by burning fuel and propelling themselves forward at an extremely high velocity.
FAQ 3: How do we hear different sounds?
The frequency of sound waves determines the pitch we hear. Higher frequencies correspond to higher pitches, while lower frequencies correspond to lower pitches. Our brains interpret these different frequencies as distinct sounds.
FAQ 4: What are the different types of magnets?
There are two main types of magnets: permanent magnets, which retain their magnetic field indefinitely (like refrigerator magnets), and electromagnets, which only exhibit magnetic properties when an electric current is flowing through them (like the electromagnets used in MRI machines).
FAQ 5: How is electricity generated?
There are many ways to generate electricity, but some common methods include converting mechanical energy (like the movement of water in a hydroelectric dam) or chemical energy (like the burning of fossil fuels) into electrical energy through generators.

