
The Digital Revolution (Late 20th Century): Transforming Our World
The Digital Revolution, which began in the late 20th century, represents a significant turning point in human history, fundamentally altering how we communicate, work, and live. This era, characterized by the shift from analog and mechanical technologies to digital technologies, has transformed every aspect of society, from personal interactions to global economies. The rapid advancement of digital technologies has not only enhanced productivity but also reshaped cultural norms and social structures. This comprehensive write-up explores the origins, key developments, societal impacts, and future implications of the Digital Revolution, highlighting its transformative power.
Introduction: The Dawn of the Digital Age
The late 20th century marked the beginning of an unprecedented technological transformation known as the Digital Revolution. This period saw the rise of computers, the internet, and mobile devices, which collectively revolutionized the way information is created, stored, and shared. The transition from mechanical and analog systems to digital technologies has had profound implications for industries, economies, and individual lives. As we navigate this new digital landscape, it is essential to understand the origins, key milestones, and societal impacts of this revolution to appreciate its ongoing influence on our world.

Origins of the Digital Revolution
Historical Context
The roots of the Digital Revolution can be traced back to several key developments in technology and society. The invention of the transistor in 1947 marked a significant milestone, enabling the miniaturization of electronic components and paving the way for modern computing. By the 1960s, computers began to emerge as powerful tools for data processing, initially used by governments and large organizations for complex calculations and record-keeping.
The Rise of Personal Computing
The introduction of personal computers (PCs) in the 1970s and 1980s brought computing power to the masses. The launch of the Apple II in 1977 and the IBM PC in 1981 made computers accessible to households and small businesses. This democratization of technology allowed individuals to harness the power of computing for personal and professional use, leading to a surge in productivity and creativity.


The Birth of the Internet
The development of the internet in the late 1960s and its subsequent commercialization in the 1990s marked another pivotal moment in the Digital Revolution. Initially created as a means for researchers and military personnel to communicate, the internet quickly evolved into a global network that connected millions of users. The introduction of the World Wide Web by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 made it easier for individuals to access and share information, laying the groundwork for the digital economy.

Key Developments During the Digital Revolution
Advancements in Communication Technology
The Digital Revolution has fundamentally transformed communication technology. The rise of email, instant messaging, and social media platforms has changed how people interact with one another. Communication has become instantaneous and global, allowing individuals to connect across vast distances in real-time. This shift has not only facilitated personal relationships but has also transformed business practices, enabling remote work and collaboration.
The Proliferation of Mobile Devices
The advent of mobile technology, particularly smartphones, has further accelerated the Digital Revolution. The launch of the iPhone in 2007 marked a significant turning point, making powerful computing capabilities portable and accessible to a broader audience. Smartphones have become essential tools for communication, information access, and entertainment, reshaping daily life and consumer behavior.

The Impact of Social Media
Social media platforms, such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, have emerged as powerful tools for communication and self-expression. These platforms have transformed the way individuals share information, connect with others, and engage with global issues. Social media has also played a crucial role in mobilizing social movements and fostering activism, enabling individuals to organize and advocate for change on a larger scale.
The Rise of E-Commerce
The Digital Revolution has fundamentally altered the landscape of commerce. The rise of e-commerce platforms, such as Amazon and eBay, has transformed the way consumers shop, allowing for convenient access to a vast array of products and services. This shift has not only changed consumer behavior but has also reshaped traditional retail models, prompting businesses to adapt to the digital marketplace.
Societal Impacts of the Digital Revolution
Changes in Work and Employment
The Digital Revolution has brought about significant changes in the nature of work and employment. Automation and digital technologies have transformed industries, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. However, this shift has also raised concerns about job displacement and the future of work. As machines and algorithms take over routine tasks, workers must adapt to new roles that require digital skills and creativity.
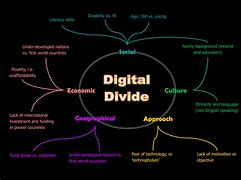
The Digital Divide
While the Digital Revolution has created new opportunities, it has also highlighted disparities in access to technology. The digital divide refers to the gap between those who have access to digital technologies and those who do not. This divide can exacerbate existing inequalities, limiting opportunities for education, employment, and social participation for marginalized communities. Addressing the digital divide is essential to ensure that all individuals can benefit from the advancements of the digital age.
Privacy and Security Concerns
The proliferation of digital technologies has raised important questions about privacy and security. As individuals share personal information online, concerns about data breaches, surveillance, and identity theft have become increasingly prominent. The Digital Revolution has necessitated discussions about the ethical implications of technology and the need for robust regulations to protect individuals’ rights and privacy.
Cultural Shifts
The Digital Revolution has also led to significant cultural shifts. The way we consume media, access information, and engage with art and culture has changed dramatically. Traditional media outlets have been disrupted by digital platforms, leading to the rise of user-generated content and new forms of storytelling. This democratization of media has empowered individuals to share their voices and perspectives, fostering diversity and creativity.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Impact of the Digital Revolution
The Digital Revolution has fundamentally transformed our world, reshaping how we communicate, work, and interact with one another. From the rise of personal computing to the proliferation of the internet and mobile devices, this era has ushered in unprecedented changes that continue to shape our lives. As we navigate the complexities of the digital age, it is essential to recognize both the opportunities and challenges presented by these advancements. The Digital Revolution is not merely a historical event; it is an ongoing process that will continue to influence the future of humanity.
FAQs
What is the Digital Revolution?
The Digital Revolution refers to the transition from analog and mechanical technologies to digital technologies, characterized by the rise of computers, the internet, and mobile devices.
When did the Digital Revolution begin?
The Digital Revolution began in the late 20th century, with significant developments occurring from the 1970s onward, particularly with the introduction of personal computers and the internet.
What are some key milestones of the Digital Revolution?
Key milestones include the invention of the transistor (1947), the development of the first personal computers (1970s), the creation of the World Wide Web (1989), and the launch of smartphones (2007).
How has the Digital Revolution impacted communication?
The Digital Revolution has transformed communication by enabling instant and global connectivity through email, social media, and messaging apps, facilitating personal and professional interactions.
What are the implications of the Digital Revolution for the workforce?
The Digital Revolution has led to changes in the nature of work, with automation and digital technologies reshaping industries. While it has increased efficiency, it has also raised concerns about job displacement and the need for new skills.
What is the digital divide?
The digital divide refers to the gap between individuals who have access to digital technologies and those who do not, which can exacerbate existing inequalities in education, employment, and social participation.
How has the Digital Revolution affected privacy and security?
The Digital Revolution has raised concerns about privacy and security, as individuals share personal information online. This has necessitated discussions about data protection, surveillance, and the ethical implications of technology.
Further Reading
For those interested in exploring the Digital Revolution further, the following resources provide valuable insights:
- Wikipedia: Information Age
- WorldAtlas: What Was the Digital Revolution?
- Dapth Insights: The Ultimate Guide to the Digital Revolution
- MinnaLearn: What is the Digital Revolution?
- DevX: Digital Revolution – Glossary
These resources offer a deeper understanding of the Digital Revolution’s historical context, technological advancements, and societal impacts.

