Ever wondered how bats navigate in total darkness? They use sound waves to “see.” Ultrasonic sensors work the same way — by sending and receiving sound waves beyond human hearing. In this guide, we’ll walk through how to interface an ultrasonic sensor with an Arduino Uno, write the code, and measure distances in centimeters, meters, and even kilometers.
Whether you’re building a smart robot, a parking system, or a motion detector, this is a core skill every maker should know.
What Is an Ultrasonic Sensor?
An ultrasonic sensor is an electronic device that measures distance by sending out ultrasonic waves and measuring the time it takes for the echo to return.
The most common model is the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, which has:
- Trigger pin: sends out the sound pulse
- Echo pin: receives the reflected pulse
- VCC: power pin (usually 5V)
- GND: ground pin
It’s like shouting into a canyon and measuring how long it takes for the echo to bounce back — simple but clever!
How It Works (In Plain English)
Here’s what happens step by step:
- The Arduino sends a signal to the sensor’s Trigger pin.
- The sensor emits an ultrasonic pulse.
- That pulse hits an object and reflects back.
- The Echo pin receives the returning sound wave.
- The Arduino calculates the distance using the time difference.
The math is simple:
Distance = (Time × Speed of Sound) / 2
Since sound travels at about 343 m/s, this formula gives very accurate results — perfect for most DIY projects.
Components You’ll Need
To get started, gather the following:
- Arduino Uno board
- HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
- Jumper wires (male to female)
- Breadboard
- USB cable (for programming)
- Laptop or PC with Arduino IDE installed
That’s it! No fancy equipment needed — just basic tools.
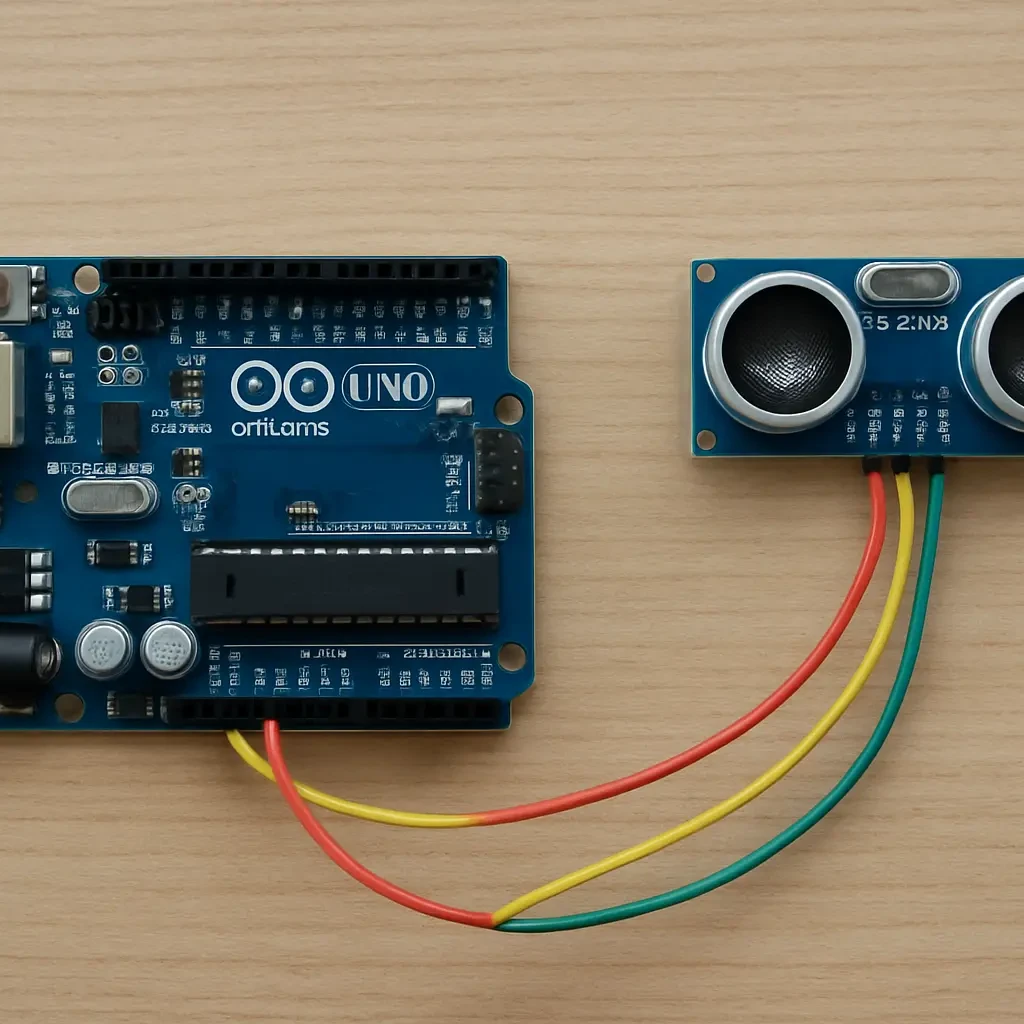
Wiring the Ultrasonic Sensor to Arduino
Connecting the sensor is easy. Here’s the standard setup:
- VCC → 5V on Arduino
- GND → GND
- Trig → Digital Pin 2
- Echo → Digital Pin 3
Make sure your connections are firm and correct. One loose wire can mess up your readings!
Breadboard View
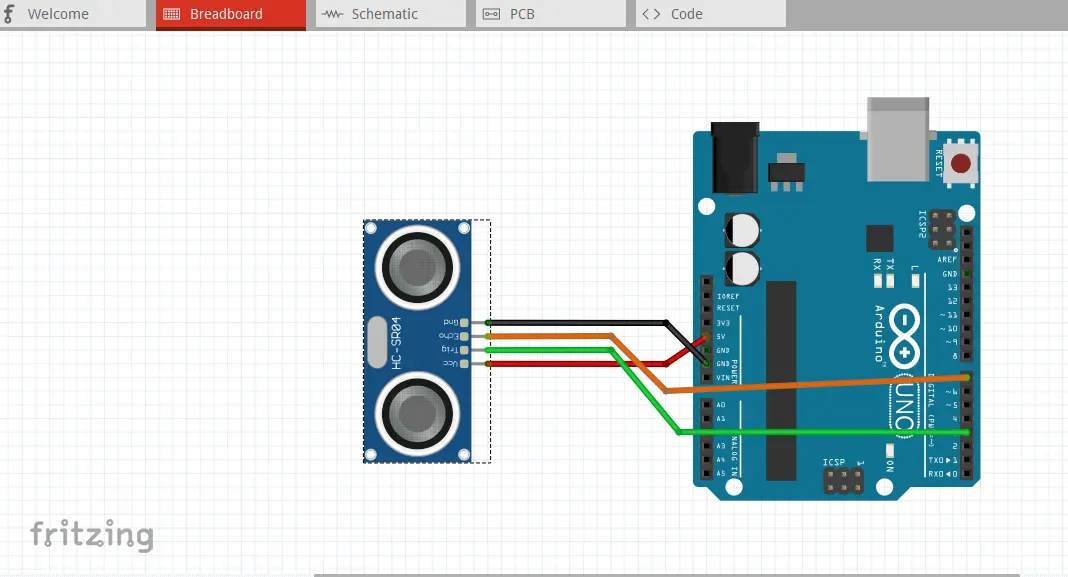
Schematic Diagram

Writing the Code
Now comes the fun part — programming. Open your Arduino IDE and type in the following code:


Upload the sketch, open your Serial Monitor, and watch your Arduino display distances in cm, m, and km in real time!
Testing and Calibration
Place an object in front of the sensor and gradually move it closer or farther away. You’ll notice the readings change dynamically.
If your readings seem off:
- Double-check your wiring.
- Ensure your object is large and flat (like a book or box).
- Avoid soft materials that absorb sound.
Small adjustments can make a big difference in accuracy.
Real-Life Applications of Ultrasonic Sensors

You’ll find ultrasonic sensors everywhere! Here are a few ideas:
- Smart parking systems — detect vehicles and empty spots.
- Obstacle-avoiding robots — sense distance and change direction.
- Water level detection — monitor tank levels without contact.
- Proximity alarms — trigger a buzzer when someone comes close.
Think of it as your electronic version of echolocation — just like bats, but smarter.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No reading on Serial Monitor | Wrong COM port | Select the correct port in Tools > Port |
| Constant 0 or max reading | Loose connection | Check wiring |
| Inaccurate values | Electrical noise | Add a small capacitor (100nF) between VCC and GND |
| Unstable readings | Interference | Use a stable power source or shield the sensor |
FAQs
1. Can ultrasonic sensors detect transparent objects?
Not reliably. They work best on solid, flat surfaces because sound waves pass through glass or thin materials.
2. How far can the HC-SR04 measure?
It typically measures between 2 cm to 400 cm (4 meters) accurately.
3. Why does my sensor give unstable readings?
It may be due to electrical noise, reflections, or incorrect wiring. Adding a capacitor or averaging multiple readings helps.
4. Can I use multiple ultrasonic sensors on one Arduino?
Yes, just connect each sensor to different pins and modify your code accordingly.
5. What can I build with an ultrasonic sensor and Arduino?
Everything from automatic doors, smart dustbins, parking systems, and robotic distance measurement projects!
Conclusion
Interfacing an ultrasonic sensor with Arduino is one of the simplest yet most rewarding projects you can try. In just a few steps, you can make your Arduino “see” distances like a digital bat!
From robotics to home automation, the possibilities are endless. Once you master this, try combining it with LEDs, buzzers, or even servo motors to build smarter and more interactive systems.
Your next project is just a sound wave away!