
Introduction
Blockchain technology has evolved significantly since its inception as the backbone of Bitcoin. While it initially garnered attention primarily for its role in cryptocurrencies, its potential applications extend far beyond digital currencies. Today, blockchain is being explored across various sectors, including healthcare, supply chain management, finance, and even voting systems. This comprehensive write-up delves into the multifaceted applications of blockchain technology, examining its benefits, challenges, and future prospects beyond cryptocurrency.
Read The Secret Weapon That Made Nvidia the World’s Most Valuable Company
Understanding Blockchain Technology
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. This technology ensures that the recorded transactions cannot be altered retroactively, providing a high level of security and transparency. Key features of blockchain include:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases controlled by a central authority, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, reducing the risk of single points of failure.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted, ensuring data integrity.
- Transparency: All participants in the network can view the transaction history, fostering trust among users.
Applications of Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrency
1. Healthcare
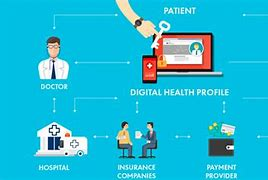
Blockchain technology is making significant strides in the healthcare sector, addressing issues related to data security, interoperability, and patient privacy. Key applications include:
- Secure Patient Data Management: Blockchain can create a secure and immutable record of patient data, allowing healthcare providers to access and share information with patient consent. This can reduce data silos and improve care coordination among providers.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain can track pharmaceuticals from manufacturers to consumers, ensuring the authenticity of drugs and preventing counterfeiting. This is particularly crucial in an industry plagued by counterfeit medications.
- Clinical Trials and Research: By utilizing blockchain, researchers can securely share data from clinical trials, ensuring transparency and integrity in the research process. This can also facilitate better patient recruitment and data management.
2. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing supply chain management by providing greater transparency and traceability. Key benefits include:
- Real-Time Tracking: Blockchain enables real-time tracking of goods as they move through the supply chain, allowing businesses to monitor inventory levels and reduce losses due to theft or spoilage.
- Smart Contracts: Automated contracts can be executed when predefined conditions are met, streamlining transactions and reducing the need for intermediaries. This can enhance efficiency and lower costs across the supply chain.
- Enhanced Collaboration: With a shared, immutable record of transactions, all parties in the supply chain can collaborate more effectively, reducing disputes and improving trust.

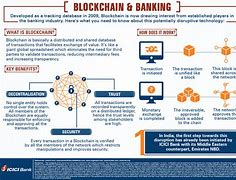
3. Finance and Banking
While cryptocurrencies are the most well-known application of blockchain in finance, the technology has broader implications:
- Cross-Border Payments: Blockchain can facilitate faster and cheaper cross-border transactions by eliminating intermediaries and reducing transaction times from days to minutes.
- Fraud Prevention: The transparency and immutability of blockchain can help prevent fraud in financial transactions by providing a clear audit trail.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Blockchain enables the creation of decentralized financial applications that allow users to lend, borrow, and trade without traditional banking intermediaries, increasing financial inclusion.
Read These Smart Home Gadgets Will Do the Work While You Relax
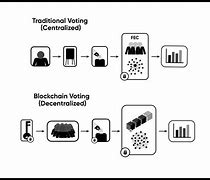
4. Voting Systems
Blockchain technology has the potential to enhance the security and transparency of voting systems:
- Secure Voting: By recording votes on a blockchain, the integrity of the electoral process can be ensured, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation.
- Voter Privacy: Blockchain can protect voter identities while ensuring that their votes are counted accurately, fostering trust in the democratic process.
- Accessibility: Blockchain-based voting systems can facilitate remote voting, making it easier for individuals with disabilities or those living abroad to participate in elections.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, blockchain technology faces several challenges:
- Scalability: Many blockchain networks struggle to handle large volumes of transactions efficiently. Solutions such as layer-2 scaling and sharding are being explored to address this issue.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The lack of clear regulations surrounding blockchain and cryptocurrencies can hinder adoption and innovation in various sectors.
- Interoperability: Different blockchain networks often operate in silos, making it difficult to share data across platforms. Efforts to develop standards and protocols for interoperability are ongoing.
Future Prospects
The future of blockchain technology is promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at overcoming existing challenges. As industries continue to explore its applications, we can expect to see:
- Increased Adoption: More organizations will recognize the benefits of blockchain, leading to widespread adoption across various sectors.
- Innovative Use Cases: As technology matures, new and innovative use cases will emerge, further expanding the horizons of blockchain applications.
- Collaboration and Standardization: Industry stakeholders will likely collaborate to establish standards and best practices, facilitating interoperability and enhancing the overall effectiveness of blockchain solutions.
Related Websites
- Deloitte: Blockchain Opportunities for Health Care – An analysis of blockchain’s potential in the healthcare sector.
- Built In: Blockchain in Healthcare – A comprehensive overview of blockchain applications in healthcare.
- The Motley Fool: Uses for Blockchain in Healthcare – Insights into the opportunities for blockchain in healthcare.
FAQs
1. What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring data integrity and transparency.
2. How is blockchain used in healthcare?
Blockchain is used in healthcare for secure patient data management, supply chain transparency, and clinical trial data sharing, among other applications.
3. What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are automated contracts that execute when predefined conditions are met, streamlining transactions and reducing the need for intermediaries.
4. What challenges does blockchain face?
Challenges include scalability, regulatory uncertainty, and interoperability among different blockchain networks.
5. What is the future of blockchain technology?
The future of blockchain technology includes increased adoption, innovative use cases, and collaboration among industry stakeholders to establish standards and best practices.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has transcended its initial association with cryptocurrency, emerging as a versatile solution with applications across various sectors. From healthcare to finance, its potential to enhance security, transparency, and efficiency is becoming increasingly recognized. As the technology matures and challenges are addressed, blockchain is poised to play a transformative role in shaping the future of numerous industries, making it a subject worth exploring beyond its cryptocurrency roots.


