Introduction
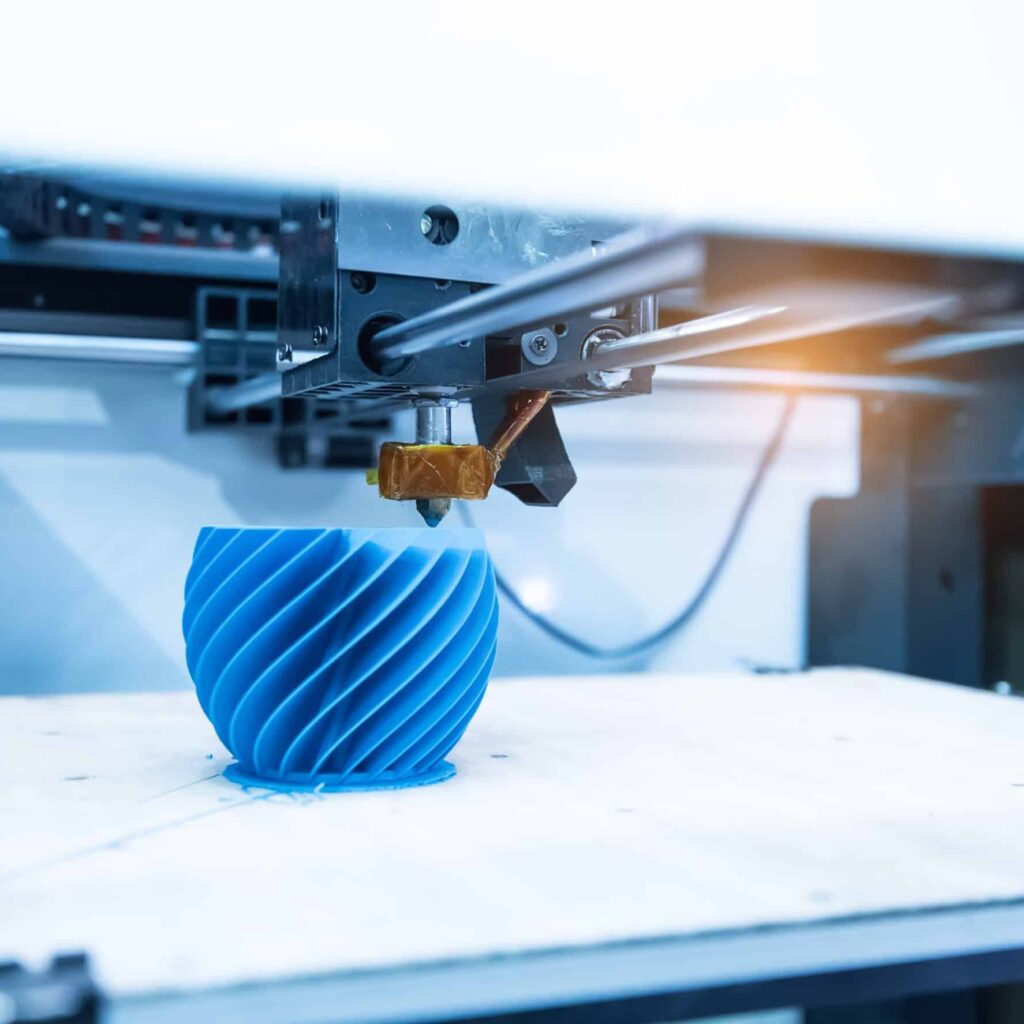
The Magic of 3D Printing: 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has transformed the way we create physical objects. From intricate prototypes to functional parts, this technology has found applications across various industries. In this article, we’ll delve into what 3D printing is, how it works, and explore some fascinating examples.
What Is 3D Printing?
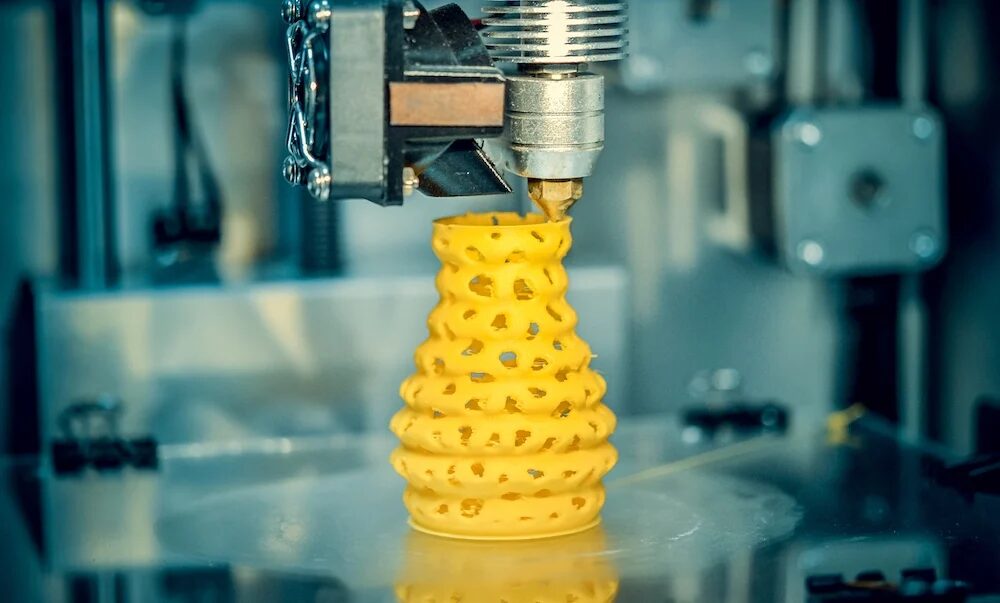

At its core, 3D printing is a process that builds three-dimensional objects layer by layer. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing, where material is removed from a solid block, 3D printing adds material to create the final product. Let’s break down the key components:
- Digital Design (CAD): The process begins with a digital 3D model created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This model serves as the blueprint for the physical object.
- Layer-by-Layer Construction: The 3D printer interprets the digital model and deposits material layer by layer. Common materials include plastics, metals, ceramics, and even food.
- Additive Process: Each layer fuses with the previous one, gradually building up the object. This additive approach allows for complex geometries that would be challenging to achieve using traditional methods.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
- Preparation: The CAD model is sliced into thin layers using specialized software. These slices guide the printer during the printing process.
- Printing: The 3D printer follows the instructions from the sliced model. It deposits material (such as melted plastic filament) onto the build platform, creating each layer.
- Cooling and Solidification: After each layer is deposited, it cools and solidifies. The printer continues this process until the entire object is complete.
- Post-Processing: Depending on the material, post-processing steps like sanding, painting, or curing may be necessary to achieve the desired finish.
Applications of 3D Printing

- Prototyping: Engineers and designers use 3D printing to quickly iterate and test prototypes before mass production.
- Customization: From personalized jewelry to tailored medical implants, 3D printing allows customization at a level previously unattainable.
- Aerospace and Automotive: Lightweight components, intricate engine parts, and even entire aircraft sections are 3D printed.
- Healthcare: Surgeons use 3D-printed models for preoperative planning, and prosthetics are customized for individual patients.
- Art and Fashion: Artists and designers create stunning sculptures, jewelry, and avant-garde fashion pieces.
Notable Examples
- MakerBot: Thingiverse, an online platform, hosts a vast collection of 3D printable design. Users can download files and bring them to life using their 3D printers.
- Automotive Industry: Companies like BMW and Ford use 3D printing for rapid prototyping and custom tooling.
- Medical Breakthroughs: Researchers have 3D printed functional organs, prosthetic limbs, and even dental implants.
Related
- 10 Free New Google AI Courses to Empower Innovators
- Top tech gadgets to upgrade your life
- Top 4 Best Antivirus Software for your PC
Conclusion
3D printing continues to evolve, pushing boundaries and enabling innovation. As technology advances, we can expect even more exciting applications in the future. Whether you’re a hobbyist, engineer, or artist, 3D printing offers a world of possibilities.
Remember, the next time you hold a 3D-printed object, you’re witnessing the fusion of creativity, precision, and technology.
