Introduction
Are you considering switching to solar energy but wondering if the financial benefits outweigh the initial investment? You’re not alone! Many homeowners and businesses hesitate because of the upfront cost, but the good news is that numerous financial incentives make solar panel installation more affordable than ever. From tax credits to rebates and net metering programs, going solar is not just an environmentally friendly decision it’s a smart financial move.

In this guide, we’ll dive into the various financial incentives available for installing solar panels and how they can significantly reduce your overall costs. Let’s get started!
Read Also: The History of Money: From Barter to Cryptocurrency
The Cost of Solar Panel Installation
Before diving into incentives, it’s crucial to understand the general cost of installing solar panels. The price depends on factors like system size, location, and installation fees. On average, residential solar panel systems cost between $15,000 and $25,000 before incentives. While this might seem expensive, the savings and incentives make solar more affordable than you think.
Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC)

One of the most significant incentives for installing solar panels in the U.S. is the Investment Tax Credit (ITC). This federal incentive allows homeowners and businesses to deduct a percentage of their solar installation costs from their federal taxes.
Read Also: Tips for Parenting a Toddler
How the ITC Works

- The ITC currently allows a 30% tax credit on the total cost of solar installation.
- This percentage will remain effective until 2032 before gradually decreasing.
- Homeowners and businesses can apply this credit to their income tax liability.
Who Qualifies for the ITC?

- Homeowners who install solar panels on their primary or secondary residences.
- Businesses that invest in commercial solar systems.
- Those who purchase (not lease) their solar energy systems.
Read Also: From Skinny to Thick: The Ever-Changing Beauty Standards for Women
State and Local Solar Incentives
Many states and local governments offer additional incentives, making solar installation even more attractive.
State Tax Credits
Some states provide tax credits similar to the federal ITC. While these vary, they can significantly reduce costs. For example:
- New York offers a 25% state tax credit, up to $5,000.
- California provides cash rebates through the California Solar Initiative.
- Massachusetts offers solar rebates and sales tax exemptions.
You may also like: How to Dress for Your Body Shape
Property Tax Exemptions

Installing solar panels can increase your home’s value, but many states exempt this added value from property taxes. This means you get the benefits of higher property value without higher tax bills.
Sales Tax Exemptions
Some states eliminate sales tax on solar equipment, lowering the overall cost of installation. For example, Florida and Arizona have 100% sales tax exemptions on solar systems.
Net Metering Programs
Net metering is another major financial benefit that allows you to sell excess solar energy back to the grid. Here’s how it works:
- Your solar system generates electricity, and any surplus power is sent to the grid.
- Your utility company credits you for this excess energy, reducing your electricity bill.
- Some states offer full retail-rate net metering, meaning you get the same rate for excess power as you pay for electricity.
Net metering policies vary by state, so check with your local utility provider for details.
Solar Renewable Energy Certificates (SRECs)
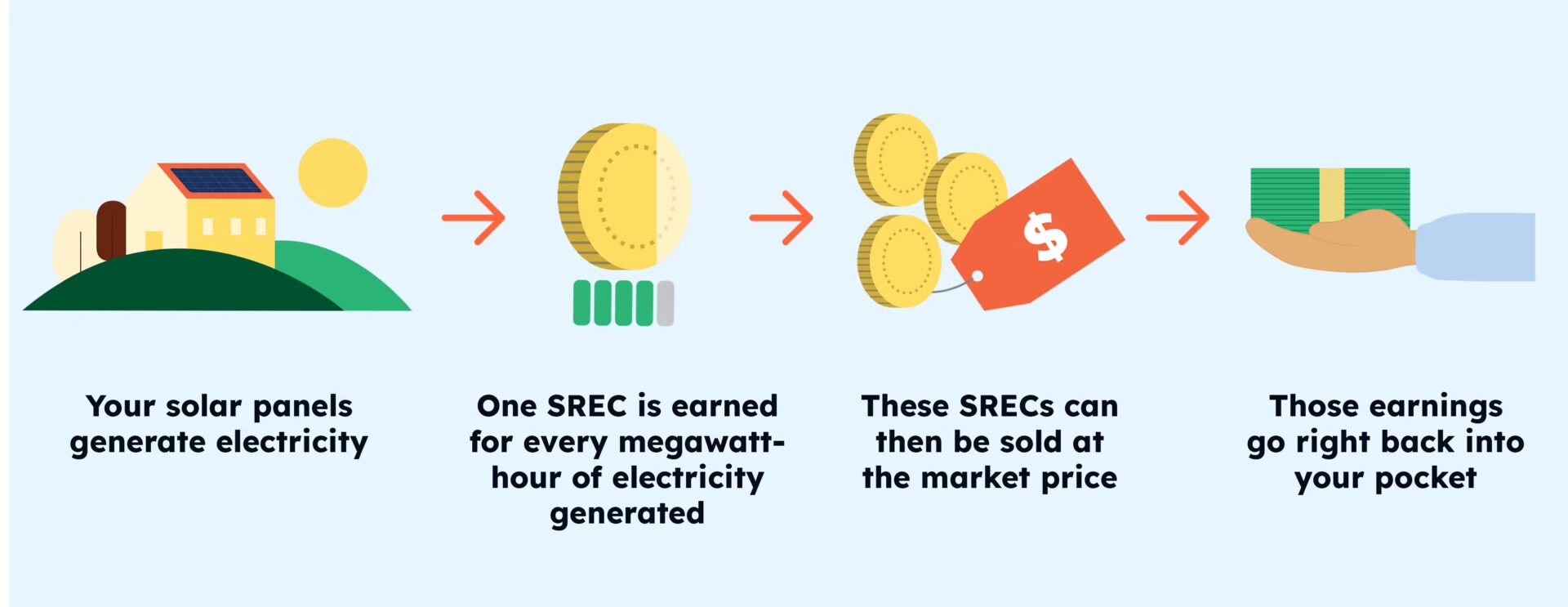
In some states, you can earn money by selling Solar Renewable Energy Certificates (SRECs). Here’s how:
- For every 1,000 kWh (kilowatt-hours) your system generates, you earn 1 SREC.
- Utility companies purchase SRECs to meet renewable energy requirements.
- The price of SRECs varies by state but can add up to significant savings.
Utility Company Rebates
Many utility companies offer rebates to encourage solar adoption. These can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars. Check with your local provider to see if rebates are available in your area.
Performance-Based Incentives (PBIs)
Unlike rebates that provide an upfront discount, Performance-Based Incentives (PBIs) pay you based on your system’s actual energy production. Some states and utilities offer these incentives, making solar even more profitable.
Solar Financing Options
If the upfront cost of solar installation is a concern, financing options can help.
Solar Loans
Solar loans allow homeowners to finance their solar systems and pay over time. Many solar loans have low-interest rates and flexible payment terms.
Solar Leases and Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)
With solar leases and PPAs, you don’t have to pay upfront for solar panels. Instead:
- A company installs and maintains the system on your property.
- You pay a fixed monthly fee (lease) or for the power generated (PPA).
- These options offer savings without ownership responsibilities.
The Long-Term Savings of Solar Panels
Investing in solar panels leads to long-term financial savings, including:
- Lower electricity bills – Solar energy reduces your dependence on grid power.
- Increased home value – Studies show homes with solar panels sell for more.
- Energy independence – You rely less on fluctuating utility rates.
Common Myths About Solar Incentives
Myth 1: Solar Incentives Are Only for Homeowners
Not true! Businesses, non-profits, and even renters (through community solar programs) can benefit from solar incentives.
Myth 2: Solar Incentives Are Going Away
While some programs may change, the federal ITC remains available, and many states are expanding solar benefits.
Myth 3: Solar Panels Don’t Work in Cloudy Areas
Even in less sunny regions, solar panels generate power. Incentives make them worthwhile regardless of location.
Conclusion
Switching to solar energy is more affordable than ever, thanks to federal tax credits, state incentives, net metering, and rebates. Whether you’re a homeowner or a business owner, these financial incentives can significantly reduce your upfront costs and provide long-term savings. With financing options available, there’s never been a better time to go solar.
FAQs
1. What is the federal tax credit for solar in 2025?
In 2025, the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) remains at 30%, helping homeowners and businesses save on solar installation costs.
2. How do I claim solar incentives on my taxes?
You can claim the solar tax credit by filing IRS Form 5695 with your federal tax return. Consult a tax professional for details.
3. Can I get solar incentives if I lease my panels?
Leasing disqualifies you from the federal ITC and other incentives since the leasing company owns the system. However, you may still benefit from lower electricity costs.
4. Do solar panels increase home value?
Yes! Studies show homes with solar panels sell for 4-5% more than homes without solar energy systems.
5. Are there incentives for battery storage systems?
Yes, some states offer rebates and tax credits for battery storage, and in some cases, batteries qualify under the federal ITC when installed with solar panels.